Difference between revisions of "Onondaga (tribe)" - New World Encyclopedia
m |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Category:Anthropology]] | [[Category:Anthropology]] | ||
| − | '''Onondaga''' | + | {{Infobox Ethnic group |
| + | |group = Onondaga | ||
| + | |image = | ||
| + | |population = unknown | ||
| + | |region1 = {{flagcountry|United States}} <small>([[New York]])</small> | ||
| + | |pop1 = | ||
| + | |ref1 = | ||
| + | |region2 = {{flagcountry|Canada}} <small>([[Ontario]])</small> | ||
| + | |pop2 = | ||
| + | |ref2 = | ||
| + | |religions = Indigenous | ||
| + | |languages = [[English language|English]], [[Onondaga language|Onondaga]] | ||
| + | |related = other [[Iroquoian]] peoples | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | The '''Onondaga''' (''Onundagaono'' or ''the People of the Hills'') are one of the original five constituent tribes of the [[Iroquois]] (''Hodenosaunee'') Confederacy. Their traditional homeland is in and around [[Onondaga County, New York]]. Being centrally located, they were the keepers of the fire in the figurative [[longhouse]], with the [[Cayuga tribe|Cayuga]] and [[Seneca_tribe|Seneca]] to their west and the [[Oneida tribe|Oneida]] and [[mohawk nation|Mohawk]] to their east. For this reason, the League of the Iroquois historically met at Onondaga, as indeed the traditional chiefs do today. | ||
| − | + | In the [[American Revolutionary War]], the Onondaga were at first officially neutral, although individual Onondaga warriors were involved in at least one raid on American settlements. The Onondaga later sided with the majority of the League and fought against the [[United States]] in alliance with the British Crown, after an American attack on their main village on April 20, 1779. Many Onondaga therefore followed [[Joseph Brant]] to [[Six Nations of the Grand River|Six Nations]], [[Ontario]] after the United States was accorded independence. Those remaining in New York are under the government of traditional chiefs nominated by [[matriarch|clan mothers]], rather than elected. | |
| − | + | On November 11, 1794, the Onondaga Nation, along with the other Haudenosaunee nations, signed the [[Treaty of Canandaigua]] with the United States. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | On March 11, 2005, the Onondaga Nation of Nedrow, New York, filed a land rights action in federal court, seeking acknowledgement of title to over 3,000 square miles of ancestral lands centering in [[Syracuse, New York|Syracuse]], [[New York]]. In doing so they hope to obtain increased influence over environmental restoration efforts at [[Onondaga Lake]] and other EPA [[Superfund]] sites in the claimed area. This lawsuit is facing a motion to dismiss based on the precedent established in the [[Cayuga nation]]'s land claim[http://www.syracuse.com/news/poststandard/index.ssf?/base/news-6/1155718727202510.xml&coll=1&thispage=2] and other defenses. | |
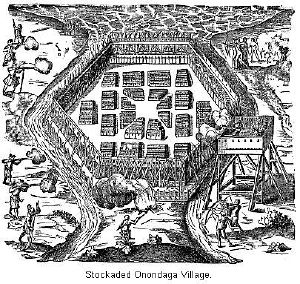
| − | + | [[Image:Onondaga Village Allen.jpg|thumb|300px|Sketch by [[Samuel de Champlain]] of his attack on an Onondaga village.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Notable Onondaga== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {{ | + | ===Modern-day=== |
| + | *[[Oren Lyons]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Onondaga bands today== | ||
| + | * [[Onondaga Nation]] in [[Nedrow, New York]] outside [[Syracuse, New York|Syracuse]] | ||
| + | * [[Onondaga Clear Sky]] and [[Bearfoot Onondaga]], both at [[Six Nations of the Grand River]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Other spellings encountered== | ||
| + | *''Onoda'gega'' | ||
| + | *''Onontakeka'' | ||
| + | *''Onondagaono'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | *[[Onondaga language]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | *Calloway, Colin G. (2004). ''First Peoples'' (2nd Ed.). Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's. ISBN 0-312-39889-1. | ||
| + | *[http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-context=dt&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U&-CONTEXT=dt&-mt_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_P001&-mt_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_P003&-tree_id=4001&-transpose=N&-redoLog=true&-all_geo_types=Y&-_caller=geoselect&-geo_id=label&-geo_id=25000US2570&-search_results=25000US2570&-format=&-_lang=en&-show_geoid=Y Onondaga Reservation, New York] United States Census Bureau | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | * [http://www.onondaganation.org Onondaga Nation web page] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/>{{Iroquois Confederacy}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Credits|Onondaga_(tribe)|133578413|}} | ||
Revision as of 14:27, 20 July 2007
| Onondaga | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | ||||||
| unknown | ||||||
| Regions with significant populations | ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Languages | ||||||
| English, Onondaga | ||||||
| Religions | ||||||
| Indigenous | ||||||
| Related ethnic groups | ||||||
| other Iroquoian peoples |
The Onondaga (Onundagaono or the People of the Hills) are one of the original five constituent tribes of the Iroquois (Hodenosaunee) Confederacy. Their traditional homeland is in and around Onondaga County, New York. Being centrally located, they were the keepers of the fire in the figurative longhouse, with the Cayuga and Seneca to their west and the Oneida and Mohawk to their east. For this reason, the League of the Iroquois historically met at Onondaga, as indeed the traditional chiefs do today.
In the American Revolutionary War, the Onondaga were at first officially neutral, although individual Onondaga warriors were involved in at least one raid on American settlements. The Onondaga later sided with the majority of the League and fought against the United States in alliance with the British Crown, after an American attack on their main village on April 20, 1779. Many Onondaga therefore followed Joseph Brant to Six Nations, Ontario after the United States was accorded independence. Those remaining in New York are under the government of traditional chiefs nominated by clan mothers, rather than elected.
On November 11, 1794, the Onondaga Nation, along with the other Haudenosaunee nations, signed the Treaty of Canandaigua with the United States.
On March 11, 2005, the Onondaga Nation of Nedrow, New York, filed a land rights action in federal court, seeking acknowledgement of title to over 3,000 square miles of ancestral lands centering in Syracuse, New York. In doing so they hope to obtain increased influence over environmental restoration efforts at Onondaga Lake and other EPA Superfund sites in the claimed area. This lawsuit is facing a motion to dismiss based on the precedent established in the Cayuga nation's land claim[1] and other defenses.
Notable Onondaga
Modern-day
- Oren Lyons
Onondaga bands today
- Onondaga Nation in Nedrow, New York outside Syracuse
- Onondaga Clear Sky and Bearfoot Onondaga, both at Six Nations of the Grand River
Other spellings encountered
- Onoda'gega
- Onontakeka
- Onondagaono
See also
- Onondaga language
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Calloway, Colin G. (2004). First Peoples (2nd Ed.). Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's. ISBN 0-312-39889-1.
- Onondaga Reservation, New York United States Census Bureau
External links
| Iroquois Confederacy | |
|---|---|
| Nations | Cayuga · Mohawk · Oneida · Onondaga · Seneca · Tuscarora |
| Topics | Economy · Languages · Mythology · Great Law of Peace · The Great Peacemaker |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.