Difference between revisions of "Imitation" - New World Encyclopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development=== | ===Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development=== | ||
| − | Paiget maintained that cognitive development could be explained in four | + | Paiget maintained that cognitive development could be explained in four distinct stages in a domain general model. These four stages, Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operations, and Formal Operations are dependent upon age and are sequential. They are as follows: |
* '''Sensorimotor''': Begins at birth and lasts until two years of age. This stage is characterized by egoccentric thinking and object permanence. Egoccentric thinking refers to the inability to perceive of a larger world separate from one's own existence. Object permanence is the understanding that objects exist independent of one's immediate sensory experience. | * '''Sensorimotor''': Begins at birth and lasts until two years of age. This stage is characterized by egoccentric thinking and object permanence. Egoccentric thinking refers to the inability to perceive of a larger world separate from one's own existence. Object permanence is the understanding that objects exist independent of one's immediate sensory experience. | ||
* '''Preoperational''': Begins in the child's second year and continues until about age 7. The Preoperational Stage is divided into two sub-stages, the Preconceptual and the Intuitive stages. The Preconceptual Stage begins around 2 years and lasts until about age four. During this time, a person learns to use symbols (eg. using words as labels). The Intuitive stage consists of using concepts and sort objects into groups by their physical characteristics. | * '''Preoperational''': Begins in the child's second year and continues until about age 7. The Preoperational Stage is divided into two sub-stages, the Preconceptual and the Intuitive stages. The Preconceptual Stage begins around 2 years and lasts until about age four. During this time, a person learns to use symbols (eg. using words as labels). The Intuitive stage consists of using concepts and sort objects into groups by their physical characteristics. | ||
* '''Concrete Operations''': This stage lasts from about 7-11 years and involves the mastery of the principles of conservation (eg., understanding that volume, mass, etc. remain constant despite perceptual changes). | * '''Concrete Operations''': This stage lasts from about 7-11 years and involves the mastery of the principles of conservation (eg., understanding that volume, mass, etc. remain constant despite perceptual changes). | ||
| − | *'''Formal Operations''': Starts after 11 years and lasts into adulthood. The Formal Operations stage is when one obtains the mastery of abstract thinking. During this stage a person should have the ability to | + | *'''Formal Operations''': Starts after 11 years and lasts into adulthood. The Formal Operations stage is when one obtains the mastery of abstract thinking. During this stage a person should have the ability to analyze problems and formulate ideas. |
===Infant Research=== | ===Infant Research=== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
=== Caveats and Criticisms === | === Caveats and Criticisms === | ||
| − | Critics of the diffusion of innovations have suggested that it is an overly simplified representation of a complex reality. A number of other phenomena can influence | + | Critics of the diffusion of innovations have suggested that it is an overly simplified representation of a complex reality. A number of other phenomena can influence adoption rates of innovation. Firstly, these customers often adapt technology to their own needs, so the innovation may actually change in nature as number of users increases. Secondly, disruptive technology may radically change the diffusion patterns for established technology by establishing a competing S-curve. Finally, path dependence may lock certain technologies in place. An example of this would be the QWERTY keyboard. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 26 November 2007
Imitation is an advanced behavior whereby an action is elicited by an indvidual's observation and subsequent replication of another's behavior. The term imitation is often used in theoretical and descriptive context. Many of the theories and ideas surrounding imitation can be applied across many disciplines.
Psychology
Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development
Paiget maintained that cognitive development could be explained in four distinct stages in a domain general model. These four stages, Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operations, and Formal Operations are dependent upon age and are sequential. They are as follows:
- Sensorimotor: Begins at birth and lasts until two years of age. This stage is characterized by egoccentric thinking and object permanence. Egoccentric thinking refers to the inability to perceive of a larger world separate from one's own existence. Object permanence is the understanding that objects exist independent of one's immediate sensory experience.
- Preoperational: Begins in the child's second year and continues until about age 7. The Preoperational Stage is divided into two sub-stages, the Preconceptual and the Intuitive stages. The Preconceptual Stage begins around 2 years and lasts until about age four. During this time, a person learns to use symbols (eg. using words as labels). The Intuitive stage consists of using concepts and sort objects into groups by their physical characteristics.
- Concrete Operations: This stage lasts from about 7-11 years and involves the mastery of the principles of conservation (eg., understanding that volume, mass, etc. remain constant despite perceptual changes).
- Formal Operations: Starts after 11 years and lasts into adulthood. The Formal Operations stage is when one obtains the mastery of abstract thinking. During this stage a person should have the ability to analyze problems and formulate ideas.
Infant Research
Animal Research
Neuroscience
Recent work in neuroscience suggests that there are specific mechanisms for imitation in the human brain. It has been proposed that there is a system of "mirror neurons". These mirror neurons fire both when an animal performs an action and when the animal observes the same action performed by another animal, especially with a conspecific animal. This system of mirror neurons have been observed in humans, primates, and certain birds. In humans, mirror neurons are localized in Broca's area and the inferior parietal cortex of the brain. Some scientists consider mirror neurons to be one of the most important findings of neuroscience in the last decade.
Anthropology
In anthropology, diffusion theories account for the phenomenon of cultures imitating the ideas or practices of others. Some theories contend that all cultures imitate ideas from one or a several original cultures, possibly creating a series of overlapping cultural circles. Evolutionary diffusion theory affirms that cultures are influenced by one another, but also claims that similar ideas can be developed in isolation of one another.
Sociology
The study of the diffusion of innovation is the study of how, why, and at the rate at which new ideas and technology spread through cultures.
Theories of Innovation Diffusion
French sociologist Gabriel Tarde originally claimed that sociology was based on small psychological interactions among individuals, with the fundamental forces being imitation and innovation.
Diffusion of innovations theory was formalized by Everett Rogers in his book called Diffusion of Innovations (1962). Rogers stated that individuals who adopt any new innovation or idea could be categorized as innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards. Each adopter's willingness and ability to adopt an innovation would depend on their awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption. Some of the characteristics of each category of adopters include:
- innovators - venturesome, educated, multiple info sources, greater propensity to take risk
- early adopters - social leaders, popular, educated
- early majority - deliberate, many informal social contacts
- late majority - skeptical, traditional, lower socio-economic status
- laggards - neighbors and friends are main info sources, fear of debt
Rogers also proposed a five stage model for the diffusion of innovation:
- Knowledge - learning about the existence and function of the innovation
- Persuasion - becoming convinced of the value of the innovation
- Decision - committing to the adoption of the innovation
- Implementation - putting it to use
- Confirmation - the ultimate acceptance or rejection of the innovation
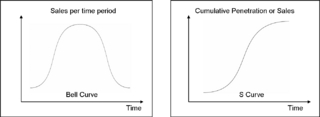
The S-Curve and technology adoption
Rogers theorized that innovations would spread through society in an S curve, as the early adopters select the technology first, followed by the majority, until a technology or innovation is commonplace.
The speed of technology adoption is determined by two characteristics p, which is the speed at which adoption takes off, and q, the speed at which later growth occurs. A cheaper technology might have a higher p, for example, taking off more quickly, while a technology that has network effects (e.g. a fax machine, where the value of the item increases as others get it) may have a higher q.
Caveats and Criticisms
Critics of the diffusion of innovations have suggested that it is an overly simplified representation of a complex reality. A number of other phenomena can influence adoption rates of innovation. Firstly, these customers often adapt technology to their own needs, so the innovation may actually change in nature as number of users increases. Secondly, disruptive technology may radically change the diffusion patterns for established technology by establishing a competing S-curve. Finally, path dependence may lock certain technologies in place. An example of this would be the QWERTY keyboard.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Rogers, Everett M. (1962). Diffusion of Innovation. New York, NY: Free Press.
- Rogers, Everett M. (2003). Diffusion of Innovation, Fifth Edition. New York, NY: Free Press. ISBN 0-7432-2209-1.
* Imitation in Animals: Evidence, Functions, and Mechanisms
External links
- Federal Reserve of Dallas 1996 Annual Report on Innovation
- The Pencil Metaphor on diffusion of innovation particularly ICT in education
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.