Difference between revisions of "Dentistry" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) (added claimed tag) |
|||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
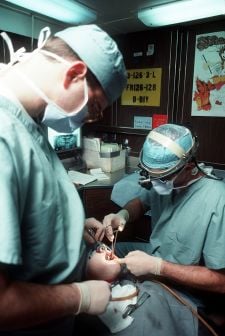
| − | + | [[Image:Dental surgery aboard USS Eisenhower, January 1990.JPEG|thumb|right|225px|A dentist and dental assistant perform surgery on a patient.]] | |
| − | [[Image:Dental | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Dentistry''' is the science and profession concerned with the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of [[disease]]s, abnormalities, or other conditions of the [[teeth]], [[gum]]s, and adjacent structures of the oral cavity. This autonomous branch of biomedical science includes such activities as treating dental decay, oral surgery, extraction of decayed teeth, straightening teeth and repositioning them for normal occlusion, treatment of diseases of the tissues surrounding teeth, and preventive actions such as cleaning teeth and applying fluoride compounds to improve resistance to decay. As with [[medicine]], dentistry has a number of specialized fields, as well as general practitioners. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | The art or science of treating conditions of the teeth and related structures in the mouth is an ancient one, with writing references tracing back at least 5,000 years. | |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Dentistry represents a field designed to add to human well-being and to joy. Good dental health itself is often tied to personal responsibility, as it relates to such actions as good [[nutrition]] ([[sugar]] consumption is correlated with cavities), brushing one's teeth, regular dental checkups, and so forth. In recent years, dentists have placed a greater emphasis on prevention. | ||
| − | + | ==Overview== | |
| + | The American Dental Association defines dentistry as the:<blockquote> | ||
| + | evaluation, diagnosis, prevention and/or treatment (nonsurgical, surgical or related procedures) of diseases, disorders and/or conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and/or the adjacent and associated structures and their impact on the human body; provided by a dentist, within the scope of his/her education, training, and experience, in accordance with the ethics of the profession and applicable law (As adopted by the 1997 ADA House of Delegates). | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
| − | + | A [[dentist]] is a healthcare professional qualified to practice dentistry. Typically this qualification is achieved after graduating with a degree of either Doctor of Dental Surgery ([[Doctor of Dental Surgery|DDS]]), Doctor of Dental Medicine ([[Doctor of Dental Medicine|DMD]]), Bachelor of Dentistry ([[BDent]]), Bachelor of Dental Science ([[BDSc]]), or Bachelor of Dental Surgery/Chirurgiae ([[BDS]]) or ([[BChD]]) or equivalent. | |
| − | + | Dentists can (and often do) further their training in one or more specialty areas (such as surgery, endodontics, orthodontics, etc.) Hence, there can be a great deal of variation between the level of skill in different disciplines from dentist to dentist. | |
| − | [[ | + | General practitioners, unlike specialists, offer general service and can decide which services they will provide and which they will refer to specialists. It is important to note that most general practitioners perform restorative, prosthetic, routine endodontic therapy, routine periodontal therapy, and simple exodontia, as well as performing examinations. Others are comfortable treating more complex cases, as well as placing implants and extracting third molars, among many other procedures frequently referred to specialists. Dentists often delegate the task of cleaning teeth to their [[dental hygienist]]s and other support staff. |
| − | [[ | + | ==Specialties== |
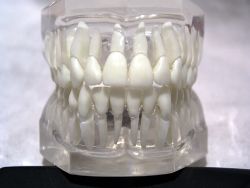
| + | [[Image:Teeth model front.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Development of teeth sculpture is a major improvement among dentistry.]] | ||
| + | The American Dental Association recognizes nine dental specialities (ADA 2007). | ||
| − | + | *'''Dental Public Health'''. Dental public health is a specialty concerend with preventing and controlling dental diseases and advancing dental heath through organized community efforts (ADA 2007). Included in this field is public dental health education, applied research, and preventing dental diseases on a community basis. | |
| − | + | *'''Endodontics'''. [[Endodontics]], from the Greek ''endo'' (inside) and ''odons'' (tooth), is the specialist sub-field of dentistry that deals with the [[pulp (tooth)|tooth pulp]] and the tissues surrounding the root of a [[tooth]]. The pulp (containing [[nerve]]s, arterioles and venules as well as lymphatic tissue and fibrous tissue) can become diseased or injured, and is often unable to repair itself; if it dies, endodontic treatment is required. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | *'''Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology'''. Oral and maxillofacial pathology deals with the study, diagnosis, management, and sometimes the treatment of oral and maxillofacial related diseases. | |
| − | + | *'''Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology'''. this specialty is concerned with the development and production of images and data that are produced when radiant energy is used for diagnosis and treament of conditions of hte oral and maxillofacial area (ADA 2007). | |
| − | + | *'''Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery'''. This specialty is involved with the diagnosis and surgical treament of conditiosn of the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial area, including both functional and aesthetic aspects (ADA 2007). for example, it would include extractions, facial surgery, and implants. | |
| − | + | *'''Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics'''. Orthodontics' is a specialty of [[dentistry]] that is concerned with the study and treatment of [[malocclusion]]s (improper bites), which may be a result of [[tooth]] irregularity, disproportionate [[jaw]] relationships, or both. The word comes from the Greek words ''ortho'' meaning straight and ''odons'' meaning tooth. Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics deals not only with diagnosis, prevention, and correction of malocclusion, but also with the neuromuscular and skeletal abnormalities of the developing or mature orofacial structures (ADA 2007). Orthodontic treatment can be carried out for purely aesthetic reasons—improving the general appearance of patients' teeth and face for cosmetic reasons—but treatment is often prescribed for practical reasons, providing the patient with a functionally improved bite ''(occlusion)''. | |
| − | + | *'''Pediatric Dentistry'''. This is an age-defined specialty that provides preventive and therapeutic oral health care for infants and children through adolescence (ADA 2007). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''Periodontics'''. Periodontology or periodontics is that specialty of dentistry that is involved with the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases of the supporting and surrounding structures of [[tooth|teeth]] and diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the [[periodontium]], which includes the [[gingiva]] (gums), [[alveolar bone]], [[cementum]], and the [[periodontal ligament]]. The word comes from the [[Greek language|Greek]] words ''peri'' meaning around and ''odons'' meaning tooth. Literally taken, it means study of that which is "around the tooth." | |
| − | * | + | *'''Prosthodontics'''. A prosthodontist is a dentist who specializes in prosthodontics, the specialty of implant, esthetic, and reconstructive dentistry. Prosthodontists specialize in the restoration of oral function by creating [[prostheses]] and restorations (i.e. complete [[dentures]], [[Crown (dentistry)|crowns]], implant retained/supported restorations). Cosmetic dentistry, implants and joint problems all fall under the field of prosthodontics. Some prosthodontists further their training in oral and maxillofacial prosthodontics, a discipline concerned with the replacement of missing facial structures. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | To become a specialist typically requires one to train in a residency or advanced graduate training program. Once residency is completed, the doctor is granted a certificate of specialty training. Many specialty programs have optional or required advanced degrees such as (MD/MBBS specific to Maxillofacial Surgery), MS, or PhD. | |
| − | + | ====Other subdivisions in dentistry==== | |
| − | + | Two other post-graduate formal advanced education programs, [[General Practice Residency]] (advanced clinical and didactic training with intense hospital experience) and [[Advanced Education in General Dentistry]] (advanced training in clinical dentistry), are recognized by the American Dental Association but do not lead to specialization. | |
| − | + | Other dental education exists where no post-graduate formal university training is required: [[cosmetic dentistry]], [[dental implant]], [[Temporomandibular joint disorder|temporo-mandibular joint therapy]]. These usually require the attendance of one or more continuing education courses. There are restrictions on allowing these dentists to call themselves specialists in these fields. The specialist titles typically are registrable titles and controlled by the local dental licensing bodies. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Forensic odontology]] consists of the gathering and use of dental evidence in law. This may be performed by any dentist with experience or training in this field. The function of the forensic dentist is primarily documentation and verification of identity. | |
| − | + | [[Geriatric dentistry]] or geriodontics is the delivery of dental care to older adults involving the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of problems associated with normal aging and age-related diseases as part of an interdisciplinary team with other health care professionals. | |
| − | + | [[Veterinary dentistry]], a specialty of [[veterinary medicine]], is the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==History== |
| − | + | [[Image:Johann Liss 002.jpg|thumb|right|200px|''Farmer at the dentist'', [[Johann Liss]], c. 1616-17.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Evidence has been found of teeth having been drilled dating back perhaps 9,000 years ago (Coppa et al. 2006; CBC 2006). This is based on the finding of nearly perfect holes drilled into the teeth of nine skulls from a [[Pakistan]]i graveyard that were carbon-dated to between 5500 B.C.E. and 7000 B.C.E. It is believed the drill bits were made out of tiny pieces of flint and manipulated with tiny bows, with the holes created impressive for their being so well done and even in the large molars in the back. | |
| − | + | The earliest written record of dentistry appears to be a [[Sumeria]]n text from 5000 B.C.E. that describes "tooth worms" as the causal agent of the dental decay (ADA 2007). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Hesy-Re (or Hesi-Re) is often called "the first dentist" (ADA 2007; Orchardson 2001). He lived in [[Egypt]] and died about 2600 B.C.E..E. His tomb has an inscription stating" the greatest of those who deal with teeth, and of physicians" (ADA 2007; Orchardson 2001). | |
| − | + | A finding dated to about 2750 B.C.E.. in Egypt suggests a surgical procedure, with a mandible with two perforations below the root of the first molar suggesting drainage of an abscessed tooth, as well as gold wires found holding two teeth (IDA 2007). | |
| − | + | The [[Ebers papyrus]], a huge roll of more than 20 meters long and 30 cm wide, also discusses dental diseases and treatments (Arab 2017; ADA 2007). This text traces to about 1700 to 1550 B.C.E., although there are suggestions of dates as early as 3000 B.C.E. (Arab 2017). Some information contained in the [[Edwin Smith Papyrus]], dated to about 1600 B.C.E., also deals with treatment of several dental ailments (Arab 2017). [[Hammurabi's Code]] contains some references to dental procedures and fees (IDA 2007). Examining the remains of some [[History of ancient Egypt|ancient Egyptians]] and [[Greco-Roman]]s reveal early attempts at dental [[prosthetic]]s and [[surgery]] (Arab 2017). | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Hippocrates (ca. 460 B.C.E. – ca. 370 B.C.E.) and Aristotle (384 B.C.E. – 322 B.C.E.) both wrote about dentistry. Dentures first appeared in Sidon and Tuscany around 630 B.C.E. (Orchardson 2001). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Medieval dentistry.jpg|thumb|225px|Medieval [[dentist]] extracting a tooth. London; c. 1360-75.]] | |
| − | [[Image: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | During the Middle Early Middle Ages in Europe, dentistry was particularly practiced by monks. Orchardson (2001) states that during the Dark and Middle Ages in Europe, from about 500 C.E. to 1500 C.E., there were no real advances, but [[Islam]]ic scholars (such as Albucasis) continued to write extensively on teeth and tooth cleaning, and during this period the Hindus and Chinese advanced various dental treatments and complex surgical procedures. In 700 C.E., a medical text in [[China]] mentions a type of amalgam, a silver paste (ADA 2007). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In Europe, knowledge in dentistry would again bloom during the [[Renaissance]] (Orchardson 2001). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Historically, dental extractions have been used to treat a variety of illnesses. During the [[Middle Ages]] and through the nineteenth century, dentistry was not a profession into itself, and often dental procedures were performed by barbers or general [[physician]]s. Barbers had often assisted the monks in their surgical ministry and assumed the surgical duties when a series of papal edicts (1130 C.E. to 1163 C.E.) prohibited monks from performing any type of surgery or tooth extraction (ADA 2007). In 1210, a Guild of Barbers was established. [[Barber]]s usually limited their practice to extracting teeth, which not only resulted in the alleviation of [[Pain and nociception|pain]], but often cured a variety of ailments linked with chronic tooth [[infection]]. Instruments used for dental extractions date back several centuries. Some barbers did more complex surgical operations. In the fourteenth century, [[Guy de Chauliac]] invented the dental pelican (resembling a [[pelican]]'s beak) which was used through the late eighteenth century. The pelican was replaced by the [[dental key]] which, in turn, was replaced by modern forceps in the twentieth century. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The first book focused solely on dentistry was written by Artzney Buchlein in 1530, titled ''The Little Medicinal Book for All Kinds of Diseases and Infirmities of the Teeth''. The first dental textbook written in [[English language|English]] was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685 (BDA 2007). | |
| − | + | {{readout||right|250px|Seventeenth–century French physician [[Pierre Fauchard]] is known as "the father of modern dentistry"}} | |
| − | + | It is said that the seventeenth–century French physician [[Pierre Fauchard]] started dentistry science as we know it today, hence he was named "the father of modern dentistry." Among many of his developments were the extensive use of [[Prosthodontics|dental prosthesis]], introducing [[dental fillings]] as treatment for [[dental caries]] and stating that sugar derivate acids like [[tartaric acid]] were responsible for dental decay. His book, ''The Surgeon Dentist: A Treatise on Teeth'', was the first to describe a comprehensive system for dentistry practice (ADA 2007). | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | + | * American Dental Association (ADA). 2007. [https://www.ada.org/en/education-careers/careers-in-dentistry/general-dentistry History of dentistry]. ''American Dental Association''. Retrieved August 31, 2020. | |
| − | *[ | + | * Arab, S.M. 2017. [https://www.arabworldbooks.com/e-zine/medicine-in-ancient-egypt-part-1-of-3 Medicine in Ancient Egypt]. ''Arab World Books''. Retrieved August 31, 2020. |
| − | + | * British Dental Association (BDA). 2007. [https://bda.org/museum/the-story-of-dentistry/ancient-modern/operators-for-the-teeth Operators for the teeth]. ''British Dental Association''. Retrieved August 31, 2020. | |
| − | *[ | + | * Coppa, A., L. Bondioli, A. Cucina, D. W. Frayer, C. Jarrige, J.-F. Jarrige, G. Quivron, M. Rossi, M. Vidale, and R. Macchiarelli. [https://www.nature.com/articles/440755a Palaeontology: Early Neolithic tradition of dentistry]. ''Nature'' 440: 755-756. Retrieved August 31, 2020. |
| − | *[ | + | * Indian Dental Association (IDA), Kerala State. 2007. [http://www.idakerala.org/dentistryhome.asp#a1b Egyptians and chinese]. ''Indian Dental Association''. Retrieved August 31, 2020. |
| − | + | * Orchardson, R. 2001. "Dentistry" in ''The Oxford Companion to the Body''. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 019852403X. | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | *[http://www. | ||
| − | * | ||
{{dentistry}} | {{dentistry}} | ||
| − | + | {{Health care}} | |
| − | {{ | + | [[Category:Life sciences]][[Category:Health and disease]][[Category:Medicine]] |
| − | + | [[Category:Health care]] | |
| − | + | {{credit|Dentistry|177315909|Endodontics|176222002|Periodontology|176717375|Orthodontics|177144197|Prosthodontics|176351979}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 16:53, 26 September 2020
Dentistry is the science and profession concerned with the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases, abnormalities, or other conditions of the teeth, gums, and adjacent structures of the oral cavity. This autonomous branch of biomedical science includes such activities as treating dental decay, oral surgery, extraction of decayed teeth, straightening teeth and repositioning them for normal occlusion, treatment of diseases of the tissues surrounding teeth, and preventive actions such as cleaning teeth and applying fluoride compounds to improve resistance to decay. As with medicine, dentistry has a number of specialized fields, as well as general practitioners.
The art or science of treating conditions of the teeth and related structures in the mouth is an ancient one, with writing references tracing back at least 5,000 years.
Dentistry represents a field designed to add to human well-being and to joy. Good dental health itself is often tied to personal responsibility, as it relates to such actions as good nutrition (sugar consumption is correlated with cavities), brushing one's teeth, regular dental checkups, and so forth. In recent years, dentists have placed a greater emphasis on prevention.
Overview
The American Dental Association defines dentistry as the:
evaluation, diagnosis, prevention and/or treatment (nonsurgical, surgical or related procedures) of diseases, disorders and/or conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and/or the adjacent and associated structures and their impact on the human body; provided by a dentist, within the scope of his/her education, training, and experience, in accordance with the ethics of the profession and applicable law (As adopted by the 1997 ADA House of Delegates).
A dentist is a healthcare professional qualified to practice dentistry. Typically this qualification is achieved after graduating with a degree of either Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS), Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD), Bachelor of Dentistry (BDent), Bachelor of Dental Science (BDSc), or Bachelor of Dental Surgery/Chirurgiae (BDS) or (BChD) or equivalent.
Dentists can (and often do) further their training in one or more specialty areas (such as surgery, endodontics, orthodontics, etc.) Hence, there can be a great deal of variation between the level of skill in different disciplines from dentist to dentist.
General practitioners, unlike specialists, offer general service and can decide which services they will provide and which they will refer to specialists. It is important to note that most general practitioners perform restorative, prosthetic, routine endodontic therapy, routine periodontal therapy, and simple exodontia, as well as performing examinations. Others are comfortable treating more complex cases, as well as placing implants and extracting third molars, among many other procedures frequently referred to specialists. Dentists often delegate the task of cleaning teeth to their dental hygienists and other support staff.
Specialties
The American Dental Association recognizes nine dental specialities (ADA 2007).
- Dental Public Health. Dental public health is a specialty concerend with preventing and controlling dental diseases and advancing dental heath through organized community efforts (ADA 2007). Included in this field is public dental health education, applied research, and preventing dental diseases on a community basis.
- Endodontics. Endodontics, from the Greek endo (inside) and odons (tooth), is the specialist sub-field of dentistry that deals with the tooth pulp and the tissues surrounding the root of a tooth. The pulp (containing nerves, arterioles and venules as well as lymphatic tissue and fibrous tissue) can become diseased or injured, and is often unable to repair itself; if it dies, endodontic treatment is required.
- Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Oral and maxillofacial pathology deals with the study, diagnosis, management, and sometimes the treatment of oral and maxillofacial related diseases.
- Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology. this specialty is concerned with the development and production of images and data that are produced when radiant energy is used for diagnosis and treament of conditions of hte oral and maxillofacial area (ADA 2007).
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. This specialty is involved with the diagnosis and surgical treament of conditiosn of the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial area, including both functional and aesthetic aspects (ADA 2007). for example, it would include extractions, facial surgery, and implants.
- Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. Orthodontics' is a specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the study and treatment of malocclusions (improper bites), which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both. The word comes from the Greek words ortho meaning straight and odons meaning tooth. Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics deals not only with diagnosis, prevention, and correction of malocclusion, but also with the neuromuscular and skeletal abnormalities of the developing or mature orofacial structures (ADA 2007). Orthodontic treatment can be carried out for purely aesthetic reasons—improving the general appearance of patients' teeth and face for cosmetic reasons—but treatment is often prescribed for practical reasons, providing the patient with a functionally improved bite (occlusion).
- Pediatric Dentistry. This is an age-defined specialty that provides preventive and therapeutic oral health care for infants and children through adolescence (ADA 2007).
- Periodontics. Periodontology or periodontics is that specialty of dentistry that is involved with the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases of the supporting and surrounding structures of teeth and diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. The word comes from the Greek words peri meaning around and odons meaning tooth. Literally taken, it means study of that which is "around the tooth."
- Prosthodontics. A prosthodontist is a dentist who specializes in prosthodontics, the specialty of implant, esthetic, and reconstructive dentistry. Prosthodontists specialize in the restoration of oral function by creating prostheses and restorations (i.e. complete dentures, crowns, implant retained/supported restorations). Cosmetic dentistry, implants and joint problems all fall under the field of prosthodontics. Some prosthodontists further their training in oral and maxillofacial prosthodontics, a discipline concerned with the replacement of missing facial structures.
To become a specialist typically requires one to train in a residency or advanced graduate training program. Once residency is completed, the doctor is granted a certificate of specialty training. Many specialty programs have optional or required advanced degrees such as (MD/MBBS specific to Maxillofacial Surgery), MS, or PhD.
Other subdivisions in dentistry
Two other post-graduate formal advanced education programs, General Practice Residency (advanced clinical and didactic training with intense hospital experience) and Advanced Education in General Dentistry (advanced training in clinical dentistry), are recognized by the American Dental Association but do not lead to specialization.
Other dental education exists where no post-graduate formal university training is required: cosmetic dentistry, dental implant, temporo-mandibular joint therapy. These usually require the attendance of one or more continuing education courses. There are restrictions on allowing these dentists to call themselves specialists in these fields. The specialist titles typically are registrable titles and controlled by the local dental licensing bodies.
Forensic odontology consists of the gathering and use of dental evidence in law. This may be performed by any dentist with experience or training in this field. The function of the forensic dentist is primarily documentation and verification of identity.
Geriatric dentistry or geriodontics is the delivery of dental care to older adults involving the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of problems associated with normal aging and age-related diseases as part of an interdisciplinary team with other health care professionals.
Veterinary dentistry, a specialty of veterinary medicine, is the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals.
History
Evidence has been found of teeth having been drilled dating back perhaps 9,000 years ago (Coppa et al. 2006; CBC 2006). This is based on the finding of nearly perfect holes drilled into the teeth of nine skulls from a Pakistani graveyard that were carbon-dated to between 5500 B.C.E. and 7000 B.C.E. It is believed the drill bits were made out of tiny pieces of flint and manipulated with tiny bows, with the holes created impressive for their being so well done and even in the large molars in the back.
The earliest written record of dentistry appears to be a Sumerian text from 5000 B.C.E. that describes "tooth worms" as the causal agent of the dental decay (ADA 2007).
Hesy-Re (or Hesi-Re) is often called "the first dentist" (ADA 2007; Orchardson 2001). He lived in Egypt and died about 2600 B.C.E. His tomb has an inscription stating" the greatest of those who deal with teeth, and of physicians" (ADA 2007; Orchardson 2001).
A finding dated to about 2750 B.C.E. in Egypt suggests a surgical procedure, with a mandible with two perforations below the root of the first molar suggesting drainage of an abscessed tooth, as well as gold wires found holding two teeth (IDA 2007).
The Ebers papyrus, a huge roll of more than 20 meters long and 30 cm wide, also discusses dental diseases and treatments (Arab 2017; ADA 2007). This text traces to about 1700 to 1550 B.C.E., although there are suggestions of dates as early as 3000 B.C.E. (Arab 2017). Some information contained in the Edwin Smith Papyrus, dated to about 1600 B.C.E., also deals with treatment of several dental ailments (Arab 2017). Hammurabi's Code contains some references to dental procedures and fees (IDA 2007). Examining the remains of some ancient Egyptians and Greco-Romans reveal early attempts at dental prosthetics and surgery (Arab 2017).
Hippocrates (ca. 460 B.C.E. – ca. 370 B.C.E.) and Aristotle (384 B.C.E. – 322 B.C.E.) both wrote about dentistry. Dentures first appeared in Sidon and Tuscany around 630 B.C.E. (Orchardson 2001).

During the Middle Early Middle Ages in Europe, dentistry was particularly practiced by monks. Orchardson (2001) states that during the Dark and Middle Ages in Europe, from about 500 C.E. to 1500 C.E., there were no real advances, but Islamic scholars (such as Albucasis) continued to write extensively on teeth and tooth cleaning, and during this period the Hindus and Chinese advanced various dental treatments and complex surgical procedures. In 700 C.E., a medical text in China mentions a type of amalgam, a silver paste (ADA 2007).
In Europe, knowledge in dentistry would again bloom during the Renaissance (Orchardson 2001).
Historically, dental extractions have been used to treat a variety of illnesses. During the Middle Ages and through the nineteenth century, dentistry was not a profession into itself, and often dental procedures were performed by barbers or general physicians. Barbers had often assisted the monks in their surgical ministry and assumed the surgical duties when a series of papal edicts (1130 C.E. to 1163 C.E.) prohibited monks from performing any type of surgery or tooth extraction (ADA 2007). In 1210, a Guild of Barbers was established. Barbers usually limited their practice to extracting teeth, which not only resulted in the alleviation of pain, but often cured a variety of ailments linked with chronic tooth infection. Instruments used for dental extractions date back several centuries. Some barbers did more complex surgical operations. In the fourteenth century, Guy de Chauliac invented the dental pelican (resembling a pelican's beak) which was used through the late eighteenth century. The pelican was replaced by the dental key which, in turn, was replaced by modern forceps in the twentieth century.
The first book focused solely on dentistry was written by Artzney Buchlein in 1530, titled The Little Medicinal Book for All Kinds of Diseases and Infirmities of the Teeth. The first dental textbook written in English was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685 (BDA 2007).
It is said that the seventeenth–century French physician Pierre Fauchard started dentistry science as we know it today, hence he was named "the father of modern dentistry." Among many of his developments were the extensive use of dental prosthesis, introducing dental fillings as treatment for dental caries and stating that sugar derivate acids like tartaric acid were responsible for dental decay. His book, The Surgeon Dentist: A Treatise on Teeth, was the first to describe a comprehensive system for dentistry practice (ADA 2007).
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- American Dental Association (ADA). 2007. History of dentistry. American Dental Association. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- Arab, S.M. 2017. Medicine in Ancient Egypt. Arab World Books. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- British Dental Association (BDA). 2007. Operators for the teeth. British Dental Association. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- Coppa, A., L. Bondioli, A. Cucina, D. W. Frayer, C. Jarrige, J.-F. Jarrige, G. Quivron, M. Rossi, M. Vidale, and R. Macchiarelli. Palaeontology: Early Neolithic tradition of dentistry. Nature 440: 755-756. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- Indian Dental Association (IDA), Kerala State. 2007. Egyptians and chinese. Indian Dental Association. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- Orchardson, R. 2001. "Dentistry" in The Oxford Companion to the Body. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 019852403X.
| Dentistry |
| Recognized Specialties |
|
Endodontics - Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology - Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology - Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery - Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics - Pediatric Dentistry - Periodontics - Prosthodontics - Dental public health |
| Unrecognized Specialties |
|
Cosmetic Dentistry - Dental Implantology - Temporomandibular Joint Disorder - Geriatric dentistry |
| Other |
|
Forensic Odontology |
| |||||||||||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Dentistry history
- Endodontics history
- Periodontology history
- Orthodontics history
- Prosthodontics history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.