European Community (Union)
{{#invoke:Message box|ambox}}
The European Community within the Union
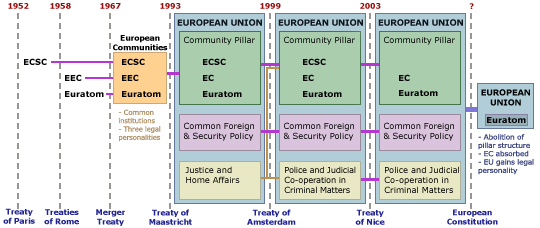
The term European Communities refers collectively to two entities — the European Economic Community (now called the European Community) and the European Atomic Energy Community (also known as Euratom) — each founded pursuant to a separate treaty in the 1950s. A third entity, the European Coal and Steel Community, was also part of the European Communities, but ceased to exist in 2002 upon the expiration of its founding treaty. Since 1967, the European Communities have shared common institutions, specifically the Council, the European Parliament, the Commission and the Court of Justice. In 1992, the European Economic Community, which of the three original communities had the broadest scope, was renamed the "European Community" by the Treaty of Maastricht.
The European Communities are one of the three pillars of the European Union, being both the most important pillar and the only one to operate primarily through supranational institutions. The other two "pillars" — Common Foreign and Security Policy, and Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters – are looser intergovernmental groupings. Confusingly, these latter two concepts are increasingly administered by the Community (as they are built up from mere concepts to actual practice).
If it had been ratified, the proposed new Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe would have abolished the three-pillar structure and, with it, the distinction between the European Union and the European Community, bringing all the Community's activities under the auspices of the European Union and transferring the Community's legal personality to the Union. There is, however, one qualification: it appears that Euratom would remain a distinct entity governed by a separate treaty (because of the strong controversy the issue of nuclear energy causes, and Euratom's relative unimportance, it was considered expedient to leave Euratom alone in the process of EU constitutional reform).
| Evolution of the structures of the European Union. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Treaties, structure and history of the European Union
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.