Difference between revisions of "Polynesia" - New World Encyclopedia
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) m |
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
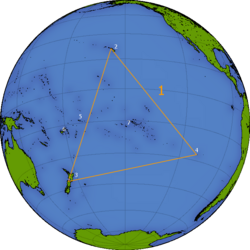
Polynesia may be described as a triangle with its corners at [[Hawaiian Islands|Hawai'i]], [[New Zealand]] and [[Easter Island]]. The other main island groups located within the Polynesian triangle are [[Samoa]], [[Tonga]], the various island chains that form the [[Cook Islands]] and [[French Polynesia]]. A Polynesian island group outside of this great triangle is [[Tuvalu]]. There are small Polynesian enclaves in the Solomons and in Vanuatu. It is also an anthropological term referring to one of the three parts of [[Oceania]] (the others being [[Micronesia]] and [[Melanesia]]). | Polynesia may be described as a triangle with its corners at [[Hawaiian Islands|Hawai'i]], [[New Zealand]] and [[Easter Island]]. The other main island groups located within the Polynesian triangle are [[Samoa]], [[Tonga]], the various island chains that form the [[Cook Islands]] and [[French Polynesia]]. A Polynesian island group outside of this great triangle is [[Tuvalu]]. There are small Polynesian enclaves in the Solomons and in Vanuatu. It is also an anthropological term referring to one of the three parts of [[Oceania]] (the others being [[Micronesia]] and [[Melanesia]]). | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Moorea baie cook.JPG|250px|thumb|Cook Bay on Moorea, French Polynesia]] | |
The Pacific Islands, except New Zealand and Easter Island, lie within the rainy tropics or the humid subtropics. In such areas there are no abrupt seasonal changes as occur in regions of temperate climate. Temperatures typically average close to 27°C (80° F) most of the year. | The Pacific Islands, except New Zealand and Easter Island, lie within the rainy tropics or the humid subtropics. In such areas there are no abrupt seasonal changes as occur in regions of temperate climate. Temperatures typically average close to 27°C (80° F) most of the year. | ||
There are coral atolls, volcanic islands, many with active volcanoes, and some of the highest mountains in the world. The vegetation varies. Soils on coral atolls are thin and sandy. Sparse vegetation consists of shrubs, small trees, grasses, and coconut palms. Continental islands have mangrove forests on the coast, palm trees further inland, and rainforest in the interior. | There are coral atolls, volcanic islands, many with active volcanoes, and some of the highest mountains in the world. The vegetation varies. Soils on coral atolls are thin and sandy. Sparse vegetation consists of shrubs, small trees, grasses, and coconut palms. Continental islands have mangrove forests on the coast, palm trees further inland, and rainforest in the interior. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
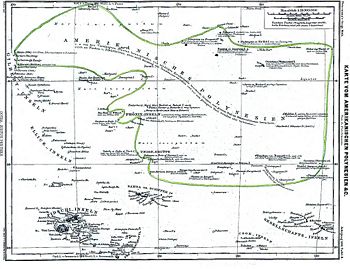
[[Image:Karte vom Amerikanischen Polynesien 1859.jpg|350px|thumb|Map of American Polynesia, [[1851]]]] | [[Image:Karte vom Amerikanischen Polynesien 1859.jpg|350px|thumb|Map of American Polynesia, [[1851]]]] | ||
| − | Polynesian | + | Polynesian history covers four eras: Exploration and settlement (1800B.C.E. to 700 C.E.), pre-European growth (700B.C.E. to 1595), European discovery and colonization(1595 to 1945), and modern times (from 1945 to present) |
| − | Maternal mitochondrial DNA analysis suggests that | + | Maternal mitochondrial DNA analysis suggests that Tongans, Samoans, Niueans, Cook Islanders, Tahitians, Hawaiians, Marquesans and Maori, are genetically linked to indigenous peoples of parts of Southeast Asia. Between about 3000 and 1000 B.C.E. speakers of Austronesian languages spread from Taiwan – into the edges of western [[Micronesia]] and on into [[Melanesia]]. In the mid second millennium BCE a distinctive culture appeared suddenly in north-west Melanesia, in the [[Bismarck Archipelago]]. This culture, known as [[Lapita]], is distinctive for its large permanent villages on beach terraces, and the making of pottery. Between about 1300 and 900 B.C.E., the Lapita culture spread 6000 kilometers east to [[Tonga]] and [[Samoa]]. |
| − | The early Polynesians were | + | The early Polynesians were adventurous seafarers. By 700C.E., the Polynesians had settled the vast [[Polynesian triangle]]. By comparison, [[Viking]] navigators first settled [[Iceland]] around 875C.E. Most evidence indicates that their motivation was to ease the demands of burgeoning populations. |
| − | Most evidence indicates that their motivation was to ease the demands of burgeoning populations. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In isolation, each local population developed politically in diverse ways, from fully-developed [[monarchy|kingdom]]s in some islands and island groups, to constantly-warring tribes or extended family groups between various sections of islands. On low islands, where communications are unimpeded, there does not appear to have developed any conflict. But on most high islands, there were warring groups inhabiting various districts, usually separated by mountain ridges, with carefully drawn lowland boundaries. Early on, however, many such islands developed a united social and political structure, usually under the leadership of a strong [[monarch]]. | |
| − | Because of the | + | The [[Marquesas Islands]] were the first Polynesian islands to be discovered by Europeans — by the [[Spain|Spanish]] navigator, [[Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira]]in 1595. Because of the scarcity of mineral or gemological resources, the exploration of Polynesia by Europeans (whose primary interest was economic), was of little more than passing interest. The great navigator Captain [[James Cook]] was the first to attempt to explore as much of Polynesia as possible. |
| − | Europeans brought a great number of changes | + | Europeans brought a great number of changes, including the introduction of alien diseases to which the Polynesians had no immunity, slavery to supply plantations in [[South America]], and an influx of Christian missionaries, many of whom regarded the Polynesians as descendants of the lost tribes of Israel. Many colonizing powers, pressured by missionaries, forcibly suppressed native cultural expression, including the use of Polynesian languages. |
| − | By the early 1900s, almost all of Polynesia was colonized or occupied | + | By the early 1900s, almost all of Polynesia was colonized or occupied by Western colonial powers. However [[Tonga]] (or the "Friendly Islands") maintained its independence, at least nominally. Meanwhile, all of the [[Polynesian outlier]]s were subsumed into the sometimes-overlapping territorial claims of Japan, the United Kingdom and France. |
| − | + | The critical attack which brought the United States into World War II, was the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, in south-central Oahu, [[Hawaii]]. A number of islands were developed by the Allies as [[military base]]s, especially by the [[United States|American]] forces, including as far east as [[Bora Bora]]. | |
| − | + | After World War II, political change came more slowly to the islands of Polynesia than to the other parts of overseas colonies of European powers. Although sovereignty was granted by royal proclamation to [[New Zealand]] as early as [[1907]], this did not go into full effect until [[1947]]. | |
Following in independence were the nations (and the sovereign powers from which they obtained complete political independence) of: [[Samoa]], as "Western Samoa" (from New Zealand) in 1962, [[Tonga]] (from the United Kingdom) in 1970, [[Tuvalu]] (from the United Kingdom) in [[1978]], the Phoenix Islands and most of the Line Islands as part of the republic of [[Kiribati]] (from the United Kingdom) in [[1979]] | Following in independence were the nations (and the sovereign powers from which they obtained complete political independence) of: [[Samoa]], as "Western Samoa" (from New Zealand) in 1962, [[Tonga]] (from the United Kingdom) in 1970, [[Tuvalu]] (from the United Kingdom) in [[1978]], the Phoenix Islands and most of the Line Islands as part of the republic of [[Kiribati]] (from the United Kingdom) in [[1979]] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 39: | ||
==Migration== | ==Migration== | ||
[[Image:hawaiiancanoe.jpg|Polynesian voyaging canoe|thumb|300px|Polynesians settled the vast Polynesian triangle by 700C.E.]] | [[Image:hawaiiancanoe.jpg|Polynesian voyaging canoe|thumb|300px|Polynesians settled the vast Polynesian triangle by 700C.E.]] | ||
| − | + | Polynesian migration is impressive considering that the islands settled are spread out over great distances — the Pacific Ocean covers nearly a half of the Earth's surface area. Most contemporary cultures, by comparison, never voyaged beyond out of sight of land. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was largely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. Explorer Captain [[James Cook]] accepted the view that migration occurred when large groups of Pacific islanders who were driven off course in storms and ended up hundreds of miles away with no idea where they were. Late nineteenth and early twentieth century writers such as [[Abraham Fornander]] and [[Stephenson Percy Smith]] told of heroic Polynesians migrating in great coordinated fleets. In the mid-twentieth century, [[Thor Heyerdahl]] argued that the Polynesians had migrated from South America on [[balsa]]-log boats. | |
| − | + | Andrew Sharp asserted, in 1963, that settlement of Polynesia had been the result of luck, random searching, and drifting, rather than as organised voyages of colonisation. In the late 1960s Dr David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand using [[stellar navigation]] without instruments. Ben Finney built a 40-foot replica of a Hawaiian double canoe and tested it in a series of sailing and paddling experiments in Hawaiian waters. At the same time, ethnographic research in the Caroline Islands in [[Micronesia]] brought to light the fact that traditional stellar navigational methods were still very much in everyday use there. This was also the case in the [[Sulu Archipelago]] in the Philippines. | |
| − | + | Polynesian navigators probably used the stars, the movement of ocean currents and wave patterns, the air and sea interference patterns caused by islands and atolls, the flight of birds, the winds and the weather. Scientists think that long-distance voyaging followed the seasonal paths of [[bird migration|birds]]. A voyage from Tahiti, the Tuamotus or the Cook Islands to New Zealand might have followed the migration of the [[Long-tailed Koel|Long-tailed cuckoo]]. It is also believed that Polynesians employed shore-sighting birds, like the [[Frigatebird|frigatebird]]. | |
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
| Line 111: | Line 86: | ||
==Issues== | ==Issues== | ||
Independence and/or increasing autonomy is not the only influence affecting modern Polynesian society. The primary driving forces are, in fact, the ever-increasing accessibility of the islands to outside influences, through improved air communications as well as through vastly improved telecommunications. The economic importance of [[tourism]] has also had a tremendous impact on the direction of the development of the various island societies. Accessibility of outside sources, as well as the tourism viability of individual islands has played an important role to which the modern culture has adapted itself to accommodating the interests of outsiders, as opposed to the influences of those intent upon promoting the retention of native traditions. Because of this, Polynesia is today an area in varying degrees of extreme cultural flux. | Independence and/or increasing autonomy is not the only influence affecting modern Polynesian society. The primary driving forces are, in fact, the ever-increasing accessibility of the islands to outside influences, through improved air communications as well as through vastly improved telecommunications. The economic importance of [[tourism]] has also had a tremendous impact on the direction of the development of the various island societies. Accessibility of outside sources, as well as the tourism viability of individual islands has played an important role to which the modern culture has adapted itself to accommodating the interests of outsiders, as opposed to the influences of those intent upon promoting the retention of native traditions. Because of this, Polynesia is today an area in varying degrees of extreme cultural flux. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Polynesia}} | {{Polynesia}} | ||
{{credit|42893118}} | {{credit|42893118}} | ||
Revision as of 07:52, 19 July 2006
Polynesia (from the Greek words meaning "many islands") is a large grouping of over 1000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The term "Polynesia" was coined by Charles de Brosses in 1756, and originally applied to all the islands of the Pacific. Jules Dumont d'Urville in an 1831 lecture to the Geographical Society of Paris proposed a restriction on its use, and also introduced the terms Micronesia and Melanesia. This division into three distinct Pacific sub-regions remains in widespread use today.
Geography
Polynesia may be described as a triangle with its corners at Hawai'i, New Zealand and Easter Island. The other main island groups located within the Polynesian triangle are Samoa, Tonga, the various island chains that form the Cook Islands and French Polynesia. A Polynesian island group outside of this great triangle is Tuvalu. There are small Polynesian enclaves in the Solomons and in Vanuatu. It is also an anthropological term referring to one of the three parts of Oceania (the others being Micronesia and Melanesia).
The Pacific Islands, except New Zealand and Easter Island, lie within the rainy tropics or the humid subtropics. In such areas there are no abrupt seasonal changes as occur in regions of temperate climate. Temperatures typically average close to 27°C (80° F) most of the year.
There are coral atolls, volcanic islands, many with active volcanoes, and some of the highest mountains in the world. The vegetation varies. Soils on coral atolls are thin and sandy. Sparse vegetation consists of shrubs, small trees, grasses, and coconut palms. Continental islands have mangrove forests on the coast, palm trees further inland, and rainforest in the interior.
History
Polynesian history covers four eras: Exploration and settlement (1800B.C.E. to 700 C.E.), pre-European growth (700B.C.E. to 1595), European discovery and colonization(1595 to 1945), and modern times (from 1945 to present)
Maternal mitochondrial DNA analysis suggests that Tongans, Samoans, Niueans, Cook Islanders, Tahitians, Hawaiians, Marquesans and Maori, are genetically linked to indigenous peoples of parts of Southeast Asia. Between about 3000 and 1000 B.C.E. speakers of Austronesian languages spread from Taiwan – into the edges of western Micronesia and on into Melanesia. In the mid second millennium B.C.E. a distinctive culture appeared suddenly in north-west Melanesia, in the Bismarck Archipelago. This culture, known as Lapita, is distinctive for its large permanent villages on beach terraces, and the making of pottery. Between about 1300 and 900 B.C.E., the Lapita culture spread 6000 kilometers east to Tonga and Samoa.
The early Polynesians were adventurous seafarers. By 700C.E., the Polynesians had settled the vast Polynesian triangle. By comparison, Viking navigators first settled Iceland around 875C.E. Most evidence indicates that their motivation was to ease the demands of burgeoning populations.
In isolation, each local population developed politically in diverse ways, from fully-developed kingdoms in some islands and island groups, to constantly-warring tribes or extended family groups between various sections of islands. On low islands, where communications are unimpeded, there does not appear to have developed any conflict. But on most high islands, there were warring groups inhabiting various districts, usually separated by mountain ridges, with carefully drawn lowland boundaries. Early on, however, many such islands developed a united social and political structure, usually under the leadership of a strong monarch.
The Marquesas Islands were the first Polynesian islands to be discovered by Europeans — by the Spanish navigator, Álvaro de Mendaña de Neirain 1595. Because of the scarcity of mineral or gemological resources, the exploration of Polynesia by Europeans (whose primary interest was economic), was of little more than passing interest. The great navigator Captain James Cook was the first to attempt to explore as much of Polynesia as possible.
Europeans brought a great number of changes, including the introduction of alien diseases to which the Polynesians had no immunity, slavery to supply plantations in South America, and an influx of Christian missionaries, many of whom regarded the Polynesians as descendants of the lost tribes of Israel. Many colonizing powers, pressured by missionaries, forcibly suppressed native cultural expression, including the use of Polynesian languages.
By the early 1900s, almost all of Polynesia was colonized or occupied by Western colonial powers. However Tonga (or the "Friendly Islands") maintained its independence, at least nominally. Meanwhile, all of the Polynesian outliers were subsumed into the sometimes-overlapping territorial claims of Japan, the United Kingdom and France.
The critical attack which brought the United States into World War II, was the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, in south-central Oahu, Hawaii. A number of islands were developed by the Allies as military bases, especially by the American forces, including as far east as Bora Bora.
After World War II, political change came more slowly to the islands of Polynesia than to the other parts of overseas colonies of European powers. Although sovereignty was granted by royal proclamation to New Zealand as early as 1907, this did not go into full effect until 1947.
Following in independence were the nations (and the sovereign powers from which they obtained complete political independence) of: Samoa, as "Western Samoa" (from New Zealand) in 1962, Tonga (from the United Kingdom) in 1970, Tuvalu (from the United Kingdom) in 1978, the Phoenix Islands and most of the Line Islands as part of the republic of Kiribati (from the United Kingdom) in 1979
The remaining islands are still under official sovereignty of the following nations: American Samoa (United States), Cook Islands (New Zealand), French Polynesia (France), Niue (New Zealand), Pitcairn (United Kingdom), Tokelau (New Zealand), Wallis and Futuna (France), Easter Island (Chile), Howland, Baker, Jarvis, and Palmyra Islands (United States).
The various outliers lie within the sovereign territory of the nations of Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands, Fiji, the Federated States of Micronesia, and the French territory of New Caledonia.
Migration
Polynesian migration is impressive considering that the islands settled are spread out over great distances — the Pacific Ocean covers nearly a half of the Earth's surface area. Most contemporary cultures, by comparison, never voyaged beyond out of sight of land.
Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was largely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. Explorer Captain James Cook accepted the view that migration occurred when large groups of Pacific islanders who were driven off course in storms and ended up hundreds of miles away with no idea where they were. Late nineteenth and early twentieth century writers such as Abraham Fornander and Stephenson Percy Smith told of heroic Polynesians migrating in great coordinated fleets. In the mid-twentieth century, Thor Heyerdahl argued that the Polynesians had migrated from South America on balsa-log boats.
Andrew Sharp asserted, in 1963, that settlement of Polynesia had been the result of luck, random searching, and drifting, rather than as organised voyages of colonisation. In the late 1960s Dr David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand using stellar navigation without instruments. Ben Finney built a 40-foot replica of a Hawaiian double canoe and tested it in a series of sailing and paddling experiments in Hawaiian waters. At the same time, ethnographic research in the Caroline Islands in Micronesia brought to light the fact that traditional stellar navigational methods were still very much in everyday use there. This was also the case in the Sulu Archipelago in the Philippines.
Polynesian navigators probably used the stars, the movement of ocean currents and wave patterns, the air and sea interference patterns caused by islands and atolls, the flight of birds, the winds and the weather. Scientists think that long-distance voyaging followed the seasonal paths of birds. A voyage from Tahiti, the Tuamotus or the Cook Islands to New Zealand might have followed the migration of the Long-tailed cuckoo. It is also believed that Polynesians employed shore-sighting birds, like the frigatebird.
Politics
Polynesia includes six independent nations (New Zealand, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, and Samoa), two political units that are parts of larger nations (Hawaii is a state of the United States, and Easter Island is part of Chile), two self-governing entities that remain linked with their former colonial power (Cook Islands and Niue with New Zealand), and five territories administered by other nations — New Caledonia, French Polynesia, and Wallis and Futuna, all administered by France, Tokelau, administered by New Zealand, and American Samoa administered by the United States. Polynesian governments vary. The independent nations replaced hereditary chiefs with constitutions providing for executives and legislatures. In Tonga, politics are controlled by a hereditary king, who serves as head of state and appoints the head of government. In the nations that have entered pacts with the United States or New Zealand, the pattern is for local self-government with matters of defence overseen by the foreign power. Internal self-government is also the rule among the territories of overseas powers, with elected legislatures and executives. Some elected representatives are sent to the national legislature in the overseas capital. French Polynesia sends one voting member to each house of the French National Assembly in Paris. The territories are dependent on the mainland government for economic subsidies, and often have little control over political decisions.
Economy
With the exception of New Zealand, most independent Polynesian islands derive much of their income from foreign aid and remittances from those who live in other countries. Some encourage their young people to go where they can earn good money to remit to their stay-at-home relatives. Many Polynesian locations, such as Easter Island, supplement this with tourism income. Some have more unusual sources of income, such as Tuvalu which marketed its '.tv' internet top-level domain name, or the Cooks that relied on stamp sales. A very few others still live as they did before western civilization encountered them.
Most Pacific Islanders grow crops for their own use. These include bananas, breadfruit, sweet potatoes, yams, cassava, and taro. Coffee plantations, introduced in the colonial era, are important in New Caledonia and Papua New Guinea, and vanilla is raised for export on Tonga. Coconut, the source of copra, or dried coconut meat, is the most common crop and is sometimes the major export. Extensive rainforests in the Solomon Islands provide forest products for export. Fishing is a source of food and a big export earner for some economies. In French Polynesia, cultured pearls are exported. Pacific Island nations have had fishing disputes with the United States and Japan.
New Caledonia has rich deposits of nickel, chromite, and iron ores. Large reserves of petroleum lie in the continental shelves along the Pacific Rim. Fields of manganese nodules, potato-sized nuggets of iron and manganese oxides that can contain copper, cobalt, and nickel have been found on patches of the ocean floor. Manufacturing is limited to handicrafts and food processing.
Polynesian countries trade with their former and current colonial powers (the United Kingdom, the United States, New Zealand, Australia, Germany, and France) as well as Canada, and increasingly, Japan. Tourism has become a big income earner. French Polynesia was the second most popular tourist destination. Japan has become the largest single source of visitors. But most tourist facilities are owned by foreigners, and much of the profit from tourism leaves the Pacific. Jobs are seasonal, and only low-skill jobs are open to islanders. Tourism can harm coral reefs and rainforests.
Shipping networks carry cargo and passengers between the hundreds of inhabited islands and atolls. Most Pacific Island nations are well served by satellite technology, and their access to telephone, television, and radio services is good. As Polynesian nations do not produce any oil or natural gas, most fuels must be imported. In rural households, wood from forests is an important source of energy.
Demographics
Polynesia divides into two distinct cultural groups, East Polynesia and West Polynesia. The culture of West Polynesia is conditioned to high populations. It has strong institutions of marriage, and well-developed judicial, monetary and trading traditions. It comprises the groups of Tonga, Niue, Samoa and the Polynesian outliers.
Eastern Polynesian cultures are highly adapted to smaller islands and atolls including the Cook Islands, Tahiti, the Tuamotus, the Marquesas, Hawaii and Easter Island. However, the large islands of New Zealand were first settled by Eastern Polynesians who adapted their culture to a non-tropical environment. Anthropologists term the Eastern Polynesian system of kinship the Hawaiian system.
Religion, farming, fishing, weather prediction, out-rigger canoe (similar to modern catamarans) construction and navigation were highly developed skills because the population of an entire island depended on them.
Trading consisted of both luxuries and mundane items. Many low-lying islands could suffer severe famine if their gardens were poisoned by the salt from the storm-surge of a hurricane. In these cases fishing, the primary source of protein, would not ease loss of food energy. Navigators, in particular, were highly respected and each island maintained a house of navigation, with a canoe-building area.
Settlements by the Polynesians were of two categories. The hamlet and the village. Size of the island inhabited determined whether or not a hamlet would be built. The larger volcanic islands usually had hamlets because of the many zones that could be divided across the island. Food and resources were more plentiful and so these settlements of four to five houses (usually with gardens) were established so that there would be no overlap between the zones. Villages, on the other hand, were built on the coasts of smaller islands and consisted of thirty or more houses. Usually these villages were fortified with walls and pallisades made of stone and wood [Encyclopedia Britannica, 1995]. However, New Zealand demonstrates the opposite; large volcanic islands with fortified villages.
Because of a strong readiness to accept new ideas and due to relatively large numbers of competitive sects of Christian missionaries in the islands, Polynesians readily adopted Christianity.
Polynesian languages are all members of the family of Oceanic languages, a sub-branch of the Austronesian language family.
Culture
Issues
Independence and/or increasing autonomy is not the only influence affecting modern Polynesian society. The primary driving forces are, in fact, the ever-increasing accessibility of the islands to outside influences, through improved air communications as well as through vastly improved telecommunications. The economic importance of tourism has also had a tremendous impact on the direction of the development of the various island societies. Accessibility of outside sources, as well as the tourism viability of individual islands has played an important role to which the modern culture has adapted itself to accommodating the interests of outsiders, as opposed to the influences of those intent upon promoting the retention of native traditions. Because of this, Polynesia is today an area in varying degrees of extreme cultural flux.
Template:Polynesia
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.