Difference between revisions of "Nail" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) (added article from Wikipedia and credit/category tags) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Claimed}}{{Contracted}} | {{Claimed}}{{Contracted}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Fingernail label.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Anatomy]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In [[anatomy]], a '''nail''' is a [[horn (anatomy)|horn]]-like structure at the end of a human's or an animal's [[finger]] or [[toe]]. See also [[claw]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Parts of the nail== | ||
| + | [[Image:Fingernails1.JPG|thumb|Fingernails]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Toenails.jpg|thumb|Toenails]] | ||
| + | Anatomically '''fingernails''' and '''toenails''', which are made of a tough [[protein]] called [[keratin]] and are produced from living skin cells in the fingers and toes, are made up of many different parts: | ||
| + | * The free edge is the part of the nail that extends past the finger, beyond the nail plate. There are no nerve endings in the nail - this is the growing part of the nail still under the skin at the nail's [[proximal]] end. | ||
| + | * [[eponychium]] or cuticle, is the fold of skin at the proximal end of the nail. | ||
| + | * [[paronychium]] is the fold of skin on the sides of the nail. | ||
| + | * [[hyponychium]] is the attachment between the skin of the finger or toe and the [[Anatomical terms of location|distal]] end of the nail. | ||
| + | * [[nail plate (anatomy)|nail plate]] is the hard and translucent portion, composed of [[keratin]]. | ||
| + | * nail bed is the adherent connective tissue that underlies the nail, often colloquially referred to as the "quick." | ||
| + | * [[lunula (anatomy)|lunula]] is the crescent shaped whitish area of the nail bed (when visible) | ||
| + | * [[nail fold]] a fold of hard skin overlapping the base and sides of a fingernail or toenail. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In common usage the word ''nail'' usually refers to the nail plate only. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- [[Image:2007-04-10 029.JPG|thumb|right|Nail with split side]] This image does not really illustrate your caption at this image size. Please consider photo editing to enhance the view. In addition, you should add text to correlate with the image.—> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:BothHand.jpg|thumb|left|Long, manicured nails are a fashion statement.]] | ||
| + | Nails grow at an average rate of 3 millimetres a month {{ref|growthrate}} Fingernails require 3 to 6 months to regrow completely. Toenails require 12 to 18 months. Actual growth rate is dependent upon age, season, exercise level, and hereditary factors. And contrary to popular belief, they do not continue to grow after death, the skin dehydrates and tightens giving the illusion that the nails grow, the same goes for hair. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This growth record can show the history of recent health and physiological imbalances, and has been used as a diagnostic tool since ancient times.{{ref|diagnoses}} Major illness will cause a [[Beau's lines|deep groove]] to form across the nails. Miscoloration, thinning, thickening, brittleness, splitting, grooves, [[Mees' lines]], [[leukonychia|small white spots]], receded lunula, [[clubbing]] (convex), flatness, spooning (concave) can indicate illness in other areas of the body, nutrient deficiencies, drug reaction or [[poisoning]], or merely local injury. Nails can also become thickened ([[Nail diseases#onychogryposis|onychogryphosis]]), loosened ([[Nail diseases#onycholysis|onycholysis]]), infected with fungus ([[onychomycosis]]) or degenerative ([[onychodystrophy]]); for further information see [[nail disease]]s. | ||
| + | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Health and care== | ||
| + | Nails can dry out, just like [[skin]]. They can also be infected: toe infections, for instance, can be caused or exacerbated by dirty [[sock]]s, specific types of aggressive exercise, tight [[footwear]] and walking unprotected in an unclean environment.{{Fact|date=July 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Manicure]]s and [[pedicure]]s are health and cosmetic procedures to groom, trim, and paint the nails and manage callouses. They require various tools such as cuticle scissors, nail scissors, [[nail clipper]]s, and [[nail file]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nail tools used by different people may transmit infections. Regarding nail tools such as files, "If they're used on different people, these tools may spread nail fungi, staph bacteria or viruses", warns Rick Lopes, a spokesperson for the California Board of Barbering and Cosmetology.{{ref|germs}} In fact, over 100 bacterial skin infections in 2000 were traced to footbaths in nail salons. To avoid this, new improved contactless tools can be used, for example, gel and cream cuticle removers instead of cuticle scissors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Biting== | ||
| + | {{main|Nail biting}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Biting the nails often indicates internal tension, [[stress (medicine)|stress]], [[boredom]], [[hunger]], or it may simply be a habit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nail biting can result in the transportation of germs that are buried under the surface of the nail into the mouth. It may also cause excessive or abnormal wear of [[tooth enamel]]{{Fact|date=September 2007}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Culture== | ||
| + | [[Image:The Ci-Xi Imperial Dowager Empress (9).PNG|thumb|right|200px|[[Empress Dowager]] [[Empress Dowager Cixi|Cixi]] displays long fingernails which reflect her high position in [[Qing Dynasty|Qing]] [[China]].]] | ||
| + | In western culture, long nails are a symbol of femininity, while short nails are a symbol of masculinity. Nail decoration is usually limited to females. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In some [[Asia]]n cultures men may also grow long fingernails, or only the nail on the [[little finger]], to show that they do not do much manual labor, but instead work in an office setting. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the 19th century in the [[Balkans]], [[white-collar]] workers, such as clerks, grew their fingernails long to distinguish them from people in lower classes who worked with their hands.<ref>''A History of Western Society.'' John McKay.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some [[guitar]] players, notably [[classical guitar|classical]] and [[fingerstyle]] players, will purposely grow long nails on the hand they use to pluck the strings. Their longer nails serve as small, easily-maneuverable guitar [[Guitar pick|picks]]. For some serious musicians, daily nail care can become a mark of pride and dedication. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In comparison, [[piano|pianists]] must keep their nails trimmed short to avoid clicking noises on the keys and avoid dangerous situations where in fast passages the nail may be caught under a key and rip off, and most [[string instrument|string]] players, such as [[violin]]ists and [[guitar]]ists, must keep at least the nails on their fretting <!-- not necessarily left hand —>hand short to allow the strings to be fingered correctly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Fashion== | ||
| + | {{main|Manicure}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Someone whose occupation is to cut any type of nail, apply artificial nails and care for nails is sometimes called a [[nailist]]. The place where a nailist works may be called a nail salon or nail shop (also "nailshop"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Painting the nails with [[nail polish]] (also known as nail lacquer) is a common practice dating back to at least 3000 B.C.E. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ornamented fake nails are sometimes used to display designs, such as stars or sparkles, on nails. They are also used to make nails look longer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Medical test == | ||
| + | Health care and pre-hospital care providers (paramedics) often use the fingernail beds as a cursory indicator of distal tissue perfusion of individuals who may be in [[Shock (medical)|shock]]. However, this test is now accepted as reliable in young children only.{{Fact|date=June 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Procedure: briefly depress the fingernail bed gently with a finger. This will briefly turn the nailbed white; the normal pink colour should be restored within a second or two. Delayed return to pink colour can be an indicator of certain shock states such as [[hypovolemia]].{{Fact|date=June 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | * [[Leukonychia]] | ||
| + | * [[Nail disease]] | ||
| + | * [[Hangnail]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="references-small" style="-moz-column-count:1; column-count:1;"><references/></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{commonscat|Nails}} | ||
| + | * {{cite journal | author = Haneke E | title = Surgical anatomy of the nail apparatus. | journal = Dermatol Clin | volume = 24 | issue = 3 | pages = 291-6 | year = 2006 | id = PMID 16798426}} | ||
| + | # {{note|growthrate}} [http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=7740 Toenail Definition - Medicine.net] | ||
| + | # {{note|diagnoses}} [http://www.aad.org/public/Publications/pamphlets/NailHealth.htm American Academy of Dermatology - Nail Health] | ||
| + | # {{note|guide}} [http://www.nails-guide.com Nails Guide - Nail Health] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{integumentary_system}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
| + | {{credit|Nail_(anatomy)|172748680}} | ||
Revision as of 01:52, 21 November 2007
In anatomy, a nail is a horn-like structure at the end of a human's or an animal's finger or toe. See also claw.
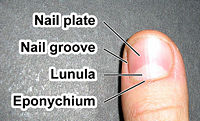
Parts of the nail
Anatomically fingernails and toenails, which are made of a tough protein called keratin and are produced from living skin cells in the fingers and toes, are made up of many different parts:
- The free edge is the part of the nail that extends past the finger, beyond the nail plate. There are no nerve endings in the nail - this is the growing part of the nail still under the skin at the nail's proximal end.
- eponychium or cuticle, is the fold of skin at the proximal end of the nail.
- paronychium is the fold of skin on the sides of the nail.
- hyponychium is the attachment between the skin of the finger or toe and the distal end of the nail.
- nail plate is the hard and translucent portion, composed of keratin.
- nail bed is the adherent connective tissue that underlies the nail, often colloquially referred to as the "quick."
- lunula is the crescent shaped whitish area of the nail bed (when visible)
- nail fold a fold of hard skin overlapping the base and sides of a fingernail or toenail.
In common usage the word nail usually refers to the nail plate only.
Nails grow at an average rate of 3 millimetres a month [1] Fingernails require 3 to 6 months to regrow completely. Toenails require 12 to 18 months. Actual growth rate is dependent upon age, season, exercise level, and hereditary factors. And contrary to popular belief, they do not continue to grow after death, the skin dehydrates and tightens giving the illusion that the nails grow, the same goes for hair.
This growth record can show the history of recent health and physiological imbalances, and has been used as a diagnostic tool since ancient times.[2] Major illness will cause a deep groove to form across the nails. Miscoloration, thinning, thickening, brittleness, splitting, grooves, Mees' lines, small white spots, receded lunula, clubbing (convex), flatness, spooning (concave) can indicate illness in other areas of the body, nutrient deficiencies, drug reaction or poisoning, or merely local injury. Nails can also become thickened (onychogryphosis), loosened (onycholysis), infected with fungus (onychomycosis) or degenerative (onychodystrophy); for further information see nail diseases. +
Health and care
Nails can dry out, just like skin. They can also be infected: toe infections, for instance, can be caused or exacerbated by dirty socks, specific types of aggressive exercise, tight footwear and walking unprotected in an unclean environment.[citation needed]
Manicures and pedicures are health and cosmetic procedures to groom, trim, and paint the nails and manage callouses. They require various tools such as cuticle scissors, nail scissors, nail clippers, and nail files.
Nail tools used by different people may transmit infections. Regarding nail tools such as files, "If they're used on different people, these tools may spread nail fungi, staph bacteria or viruses", warns Rick Lopes, a spokesperson for the California Board of Barbering and Cosmetology.[3] In fact, over 100 bacterial skin infections in 2000 were traced to footbaths in nail salons. To avoid this, new improved contactless tools can be used, for example, gel and cream cuticle removers instead of cuticle scissors.
Biting
Biting the nails often indicates internal tension, stress, boredom, hunger, or it may simply be a habit.
Nail biting can result in the transportation of germs that are buried under the surface of the nail into the mouth. It may also cause excessive or abnormal wear of tooth enamel[citation needed].
Culture
In western culture, long nails are a symbol of femininity, while short nails are a symbol of masculinity. Nail decoration is usually limited to females.
In some Asian cultures men may also grow long fingernails, or only the nail on the little finger, to show that they do not do much manual labor, but instead work in an office setting.
In the 19th century in the Balkans, white-collar workers, such as clerks, grew their fingernails long to distinguish them from people in lower classes who worked with their hands.[1]
Some guitar players, notably classical and fingerstyle players, will purposely grow long nails on the hand they use to pluck the strings. Their longer nails serve as small, easily-maneuverable guitar picks. For some serious musicians, daily nail care can become a mark of pride and dedication.
In comparison, pianists must keep their nails trimmed short to avoid clicking noises on the keys and avoid dangerous situations where in fast passages the nail may be caught under a key and rip off, and most string players, such as violinists and guitarists, must keep at least the nails on their fretting hand short to allow the strings to be fingered correctly.
Fashion
Someone whose occupation is to cut any type of nail, apply artificial nails and care for nails is sometimes called a nailist. The place where a nailist works may be called a nail salon or nail shop (also "nailshop").
Painting the nails with nail polish (also known as nail lacquer) is a common practice dating back to at least 3000 B.C.E.
Ornamented fake nails are sometimes used to display designs, such as stars or sparkles, on nails. They are also used to make nails look longer.
Medical test
Health care and pre-hospital care providers (paramedics) often use the fingernail beds as a cursory indicator of distal tissue perfusion of individuals who may be in shock. However, this test is now accepted as reliable in young children only.[citation needed]
Procedure: briefly depress the fingernail bed gently with a finger. This will briefly turn the nailbed white; the normal pink colour should be restored within a second or two. Delayed return to pink colour can be an indicator of certain shock states such as hypovolemia.[citation needed]
See also
- Leukonychia
- Nail disease
- Hangnail
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ A History of Western Society. John McKay.
- Haneke E (2006). Surgical anatomy of the nail apparatus.. Dermatol Clin 24 (3): 291-6. PMID 16798426.
- ^ Toenail Definition - Medicine.net
- ^ American Academy of Dermatology - Nail Health
- ^ Nails Guide - Nail Health
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.