Isidore of Seville
- See Isidore and Isidro for namesakes.
| Saint Isidore of Seville | |
|---|---|
| Bishop, Doctor of the Church | |
| Born | c.560 at Cartagena, Spain |
| Died | April 4, 636 at Seville, Spain |
| Venerated in | Roman Catholic Church |
| Feast | April 4 |
| Attributes | bees; bishop holding a pen while surrounded by a swarm of bees; bishop standing near a beehive; old bishop with a prince at his feet; pen; priest or bishop with pen and book; with Saint Leander, Saint Fulgentius, and Saint Florentina; with his Etymologia |
| Patronage | (only proposed, but quite well embraced) computers, the internet, students |
| Saints Portal |
Saint Isidore of Seville (Spanish: San Isidro or San Isidoro de Sevilla) (c.560 – April 4, 636) was Archbishop of Seville for more than three decades and has the reputation of being one of the great scholars of the early Middle Ages. All the later medieval history-writing of Spain were based on his histories.
At a time of disintegration of classical culture, and aristocratic violence and illiteracy, he was involved in the conversion of the royal Visigoth Arians to Catholicism, both assisting his brother Leander and continuing after his brother's death. Like Leander, he took a most prominent part in the Councils of Toledo and Seville. In all justice, it may be said that it was due to the enlightened statecraft of these two illustrious brothers, that the Visigothic legislation which emanated from these councils, is regarded by modern historians as exercising an important influence on the beginnings of representative government.
Life
Childhood and education
Isidore was born in Cartagena, Spain, to Severianus and Theodora, part of an influential family who were instrumental in the political-religious maneuvering that converted the Visigothic kings from Arianism to Catholicism, and were all awarded sainthoods:
- His elder brother Leander was his immediate predecessor in the Catholic Metropolitan See of Seville, and while in office opposed king Liuvigild
- A younger brother, St. Fulgentius, was awarded the Bishopric of Astigi at the start of the new reign of Catholic Reccared.
- His sister Florentina was a nun, and is said to have ruled over forty convents and one thousand religious.
Isidore received his elementary education in the Cathedral school of Seville. In this institution, which was the first of its kind in Spain, the trivium and quadrivium were taught by a body of learned men, among whom was the archbishop, Leander. With such diligence did he apply himself to study that in a remarkably short time mastered Latin, Greek, and Hebrew.
Whether Isidore ever embraced monastic life or not is still an open question, but though he himself may never have been affiliated with any of the religious orders, he esteemed them highly — on his elevation to the episcopate he immediately constituted himself protector of the monks and in 619 he pronounced anathema against any ecclesiastic who should in any way molest the monasteries.
Bishop of Seville
On the death of Leander, Isidore succeeded to the See of Seville.
His long incumbency in this office was spent in a period of disintegration and transition. The ancient institutions and classic learning of the Roman Empire were fast disappearing. In Spain a new civilization was beginning to evolve itself from the blending racial elements that made up its population. For almost two centuries the Goths had been in full control of Spain, and their barbarous manners and contempt of learning threatened greatly to put back her progress in civilization.
Realizing that the spiritual as well as the material well-being of the nation depended on the full assimilation of the foreign elements, St. Isidore set himself to the task of welding into a homogeneous nation the various peoples who made up the Hispano-Gothic kingdom. To this end he availed himself of all the resources of religion and education. His efforts were attended with complete success. Arianism, which had taken deep root among the Visigoths, was eradicated, and the new heresy of Acephales was completely stifled at the very outset; religious discipline was everywhere strengthened.
Second Synod of Seville (November 618 or 619)
Isidore presided over the Second Council of Seville, begun 13 November, 619, in the reign of Sisebur. The bishops of Gaul and Narbonne attended, as well as the Spanish prelates. In the Council's Acts the nature of Christ is fully set forth, countering Arian conceptions.
Fourth National Council of Toledo
At this council, begun 5 December, 633, all the bishops of Spain were in attendance. St. Isidore, though far advanced in years, presided over its deliberations, and was the originator of most of its enactments.
The council probably expressed with tolerable accuracy the mind and influence of Isidore. The position and deference granted to the king is remarkable. The church is free and independent, yet bound in solemn allegiance to the acknowledged king: nothing is said of allegiance to the bishop of Rome.
It was at the Fourth National Council of Toledo and through his influence that a decree was promulgated commanding and requiring all bishops to establish seminaries in their Cathedral Cities, along the lines of the school associated with Isidore already existing at Seville. Within his own jurisdiction he had availed himself of the resources of education to counteract the growing influence of Gothic barbarism. His was the quickening spirit that animated the educational movement of which Seville was the centre. The study of Greek and Hebrew as well as the liberal arts, was prescribed. Interest in law and medicine was also encouraged. Through the authority of the fourth council this policy of education was made obligatory upon all the bishops of the kingdom.
Works
Isidore's Latin style in the ‘’Etymologiae‘’ and elsewhere, though simple and lucid, cannot be said to be classical, affected as it was by local Visigothic traditions. It discloses most of the imperfections peculiar to all ages of transition and particularly reveals a growing Visigothic influence, containing hundreds of recognizably Spanish words — his 18th-century editor Faustino Arévalo identified 1,640 of them: Isidore can possibly be characterized as the world's last native speaker of Latin and perhaps the world's first native speaker of Spanish.
Etymologiae
Long before the Arabs had awakened to an appreciation of Greek Philosophy, he had introduced Aristotle to his countrymen. He was the first Christian writer to essay the task of compiling for his co-religionists a summa of universal knowledge, in the form of his most important work, the Etymologiae (taking its title from the method he used in the transcription of his era's knowledge). This encyclopedia — the first known to be compiled in western civilization — epitomized all learning, ancient as well as modern, forming a huge compilation of 448 chapters in 20 volumes. In it many fragments of classical learning are preserved which otherwise would have been hopelessly lost but, on the other hand, some of these fragments were lost in the first place because Isidore’s work was so highly regarded that it superseded the use of many individual works of the classics themselves, which were not recopied and have therefore been lost.
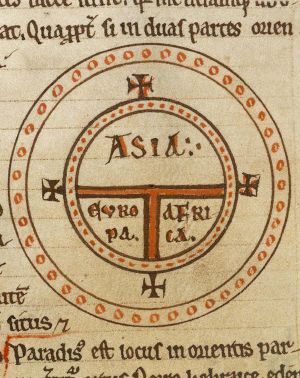
Unfortunately his classical learning failed him when it came to world geography; he misread his sources to say that the earth was flat, inventing the T and O map concept, as it is now known. For several centuries this nearly came to replace the traditional view that the earth was round, as stated for example by Bede in his The Reckoning of Time.
The fame of this work imparted a new impetus to encyclopedic writing, which bore abundant fruit in the subsequent centuries of the Middle Ages. It was the most popular compendium in medieval libraries. It was printed in at least 10 editions between 1470 and 1530, showing Isidore's continued popularity in the Renaissance. Until the 12th century brought translations from Arabic sources, Isidore transmitted what western Europeans remembered of the works of Aristotle and other Greeks, although he understood only a limited amount of Greek. The Etymologiae was much copied, particularly into medieval bestiaries.
Other works
His other works include
- his Chronica Majora (a universal history)
- De differentiis verborum, which amounts to brief theological treatise on the doctrine of the Trinity, the nature of Christ, of Paradise, angels, and men.
- a History of the Goths
- On the Nature of Things (not the poem of Lucretius)
- a book of astronomy and natural history dedicated to the Visigothic king Sisebut
- Questions on the Old Testament.
- a mystical treatise on the allegorical meanings of numbers
- a number of brief letters.
- Sententiae libri tres (Cod. Sang. 228, 9th c.)
Afterlife
Isidore was the last of the ancient Christian Philosophers, as he was the last of the great Latin Church Fathers. He was undoubtedly the most learned man of his age and exercised a far-reaching and immeasurable influence on the educational life of the Middle Ages. His contemporary and friend, Braulio. Bishop of Saragossa, regarded him as a man raised up by God to save the Spanish people from the tidal wave of barbarism that threatened to inundate the ancient civilization of Spain, The Eighth Council of Toledo (653) recorded its admiration of his character in these glowing terms: "The extraordinary doctor, the latest ornament of the Catholic Church, the most learned man of the latter ages, always to be named with reverence, Isidore". This tribute was endorsed by the Fifteenth Council of Toledo, held in 688.
- In Dante's Paradise (Paradiso' X.130), he is mentioned among theologians and doctors of the church alongside the Scot Richard of St. Victor and the Englishman Bede.
- He was canonized as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church in 1598 and declared a Doctor of the Church in 1722.
- In 2003 he was proposed as the patron saint of the Internet, but was not among the top six vote totals in an Italian language Internet poll (Google translation: [1])
See also
- Cartographer
External links
- Order of St. Isidore of Seville
- Henry Wace, Dictionary of Christian Biography
- Catholic Encyclopedia, 1913: 'Isidore of Seville'
- The Most Serene and Sovereign Order of Saint Isidore
- The Etymologiae (complete latin text)
- Jones, Peter. "Patron saint of the internet". The Telegraph, August 27, 2006 (Review of The Etymologies of Isidore of Seville, Cambridge University Press, 2006 (ISBN 0-521-83749-9))
- Shachtman, Noah. "Searchin' for the Surfer's Saint". Wired, January 25, 2002
This article incorporates text from the public-domain Catholic Encyclopedia of 1913.
ast:Isidoru de Sevilla bg:Исидор Севилски de:Isidor von Sevilla es:Isidoro de Sevilla fr:Isidore de Séville gl:Isidoro de Sevilla hr:Sveti Izidor Seviljski id:Isidore dari Sevilla ia:Isidor de Sevilla it:Sant'Isidoro di Siviglia he:איזידור מסביליה la:Isidorus Hispalensis hu:Sevillai Szent Izidor nl:Isidorus van Sevilla pl:Izydor z Sewilli pt:Isidoro de Sevilha ro:Isidor din Sevilla ru:Исидор Севильский sq:Isidori i Seviljes sk:Izidor zo Sevilly sl:Sveti Izidor Seviljski sv:Isidor av Sevilla
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.