Popular articles
Popular Articles Overall
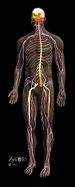
The human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, including the chemical elements, cells, and extracellular materials and the organization of these materials into tissues, organs, and systems.
The United States of America—also referred to as the United States, the USA, the U.S., America, the States, or (archaically) Columbia—is a federal republic of 50 states and the District of Columbia located primarily in central North America.
In general discussion, a nation-state is variously called a "country," a "nation," or a "state."
World War II, also WWII, or the Second World War, was a global military conflict that took place between 1939 and 1945.
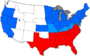
The watershed event of United States history was the American Civil War (1861–1865), fought in North America between 24 mostly northern states of the Union and the Confederate States of America, a coalition of eleven southern states.
Ancient Egypt as a general historical term broadly refers to the civilization of the Lower Nile Valley (or the Great Rift Valley) between the First Cataract and the mouths of the Nile Delta, from circa 3300 B.C.E. until the conquest of Alexander the Great in 332 B.C.E..
The Inca Civilization (called Tawantinsuyu in modern spelling, and Quechua, or Tahuantinsuyu in old spelling), was an empire located in South America from 1438 c.e. to 1533 c.e.
Birds (class Aves) are bipedal, warm-blooded, oviparous (egg-laying) vertebrates characterized primarily by feathers, forelimbs modified as wings, and a bony beak without teeth.
Globalization, as a concept, refers both to the "shrinking" of the world and the increased consciousness of the world as a whole.
Constantinople (Greek: Κωνσταντινούπολη) was the capital of the Byzantine Empire and, following its fall in 1453, of the Ottoman Empire until 1930, when it was renamed Istanbul as part of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk's Turkish national reforms.
Last month's Popular Articles
Netherlands is the European section of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which is formed by the Netherlands, the Netherlands Antilles and Aruba.
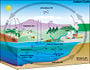
Carbon (chemical symbol C; atomic number 6) is a remarkable chemical element that plays a vital role in the structures and processes of the living and nonliving worlds.
Sun Myung Moon (문선명, 文鮮明), born February 25, 1920 (lunar: January 6, 1920), in North Pyeongan Province, which is now part of North Korea, is the founder of the Unification Church.
The Byzantine Empire is the term conventionally used to describe the Greek-speaking Roman Empire during the Middle Ages, centered at its capital in Constantinople.
The main group elements of the periodic table are groups 1, 2 and 13 through 18. Elements in these groups are collectively known as main group or representative elements.
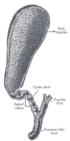
The gallbladder (also gall bladder), or cholecyst, is a pear-shaped organ that stores and concentrates bile until it is needed to aid with fat digestion.
Sigmund Freud introduced what would later come to be called the "structural theory" of psychoanalysis in his 1923 book The Ego and the Id.
Intelligent design (ID) is the view that it is possible to infer from empirical evidence that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection.
In general, the term fashion refers to a prevailing mode of expression, whether it be custom, style of dress, speech, or other.
Oxygen (chemical symbol O, atomic number 8) is the second most common element on Earth and the third most common element in the universe.