Difference between revisions of "Battle of the Alamo" - New World Encyclopedia
(Claimed) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
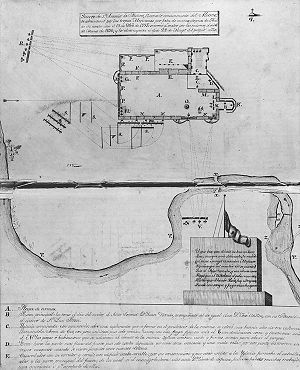
| − | {{ | + | [[Image:AlamoplanF0385.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Alamo Mission in San Antonio, Texas, by José Juan Sánchez-Navarro, 1836.]] |
| − | + | The '''Battle of the Alamo''' was a nineteenth century battle between the [[Mexico|Republic of Mexico]] and the rebel Texan forces during the latter's fight for independence - the [[Texas Revolution]]. It took place at the Alamo mission in San Antonio, Texas (then known as "San Antonio de Béxar") in February and March of 1836. The 13-day [[siege]] ended on March 6 with the capture of the mission and the death of nearly all the Texan defenders, except for a few [[slavery|slaves]], women and children. Despite the loss, the 13-day holdout stalled Mexican forces' progress and allowed [[Sam Houston]] to gather troops and supplies for his later successful battle at [[Battle of San Jacinto|San Jacinto]]. Approximately 189 defenders were attacked by about 4,000 Mexican soldiers. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The '''Battle of the Alamo''' was a | ||
| − | The battle took place at a turning point in the Texas Revolution, which had begun with the October 1835 Consultation whose delegates narrowly approved a call for rights under the [[Mexican Constitution of 1824]]. By the time of the battle, however, sympathy for declaring a [[Republic of Texas]] had grown. The delegates from the Alamo to the Constitutional Convention were both instructed to vote for independence. | + | The battle took place at a turning point in the Texas Revolution, which had begun with the October 1835 Consultation whose delegates narrowly approved a call for rights under the [[Mexican Constitution of 1824]]. By the time of the battle, however, sympathy for declaring a [[Republic of Texas]] had grown. The delegates from the Alamo to the Constitutional Convention were both instructed to vote for independence. The deaths of such popular figures as [[Davy Crockett]] and [[James Bowie|Jim Bowie]] at the Alamo contributed to how the siege has subsequently been regarded as an heroic and iconic moment in Texan and U.S. history, notwithstanding that the Alamo fell. Texas' independence and its eventual union with the U.S. would have been unlikely had Mexico succeeeded in its plan to reassert sovereignty over the territory, which later would contribute enormously to the U.S. economy. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | ==Prelude== | ||
| + | Texas was part of the Mexican colony of [[New Spain]]. After the [[Mexico|Mexican]] [[Mexican War of Independence|independence]] in 1821, Texas became part of Mexico. In 1824 it became the northern section of [[Coahuila y Tejas]]. January 3, 1823, [[Stephen F. Austin]] began a colony of 300 American families along the [[Brazos River]] in present-day Fort Bend County and Brazoria County, primarily in the area of what is now Sugar Land. | ||
| − | + | In 1835 the Mexican President and General Antonio López de Santa Anna Pérez de Lebrón, (known as Santa Anna) abolished the Constitution of 1824 and proclaimed a new constitution that increased the power of the Presidency and reduced the power of provincial governments. Since the end of hostilities with Spain ten years before, the Mexican government generally and Santa Anna in particular, had been eager to reassert control over entire country and control of Texas. This was seen as important as Santa Anna perceived the province to be vulnerable to America's westward expansion, which was in fact the case. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Mexico's new interest in Texas was not popular with the colonists, who felt themselves to be more economically and culturally linked to the United States than to Mexico. They were also used to the relative autonomy they enjoyed under the old Constitution of 1824. Santa Anna's increasingly ambitious seizure of dictatorial powers under the new constitution was causing unrest throughout Mexico. Hostilities in Texas began with the Battle of Gonzales, October 1, 1835 after which Texan rebels quickly captured Mexican positions at Goliad (La Bahía) and San Antonio. | |
| − | + | After the surrender of General [[Martín Perfecto de Cos]] and his garrison at San Antonio, there was no longer a Mexican military presence in Texas. Santa Anna decided to launch an offensive to put down the [[rebellion]]. Minister of War [[José María Tornel]] and Maj. Gen. [[Vicente Filisola]] (1789–1850) proposed a seaborne attack to Santa Anna, which would have been easier for the troops. Since 1814, sea access had been the proven means of expeditions into Texas. Santa Anna refused this plan because it would take too long and, in the meantime, the rebels in Texas might receive aid from the [[United States]]. | |
| − | + | Santa Anna assembled an estimated force of 6,100 soldiers and 20 cannons at San Luis Potosí in early 1836 and moved through [[Saltillo]], [[Coahuila]], towards Texas. His army marched across the Rio Grande through inclemental weather and snowstorms to suppress the rebellion. San Antonio de Béxar was one of his intermediate objectives; his ultimate objective was to destroy the Texas government and to restore rule of the central or "Centralist" Mexican government over a rebellious state. He had already suppressed a rebellion in the state of [[Zacatecas]] in 1835. | |
| − | Santa Anna | + | Santa Anna and his army arrived in San Antonio de Béxar on February 23, a mixed force of regular [[infantry]] and [[cavalry]] units and ''activo'' reserve infantry [[battalion]]s. They were equipped with British Baker and out-dated, short range but effective and deadly [[United Kingdom|British]] Tower Musket, Mark III, or "Brown Bess" muskets. The average Mexican soldier stood 5 feet, 1 inch; many were recent conscripts with no previous combat experience. Although well-drilled, the Mexican army discouraged individual marksmanship. Initial forces were equipped with four 7 inch howitzers, seven 4-pound, four 6-pound, four 8-pound, and two 12-pound cannons. |
| − | + | Many Mexican officers were foreign [[mercenary]] [[veteran]]s, including Vicente Filisola (Italy) and Antonio Gaona (Cuba), while General Santa Anna was a veteran of [[Mexican War of Independence]]. | |
| − | + | ==Defenders== | |
| + | {{readout||right|250px|The deaths of such popular figures as [[Davy Crockett]] and [[James Bowie{{!}}Jim Bowie]] contributed to how the Battle of the Alamo has been regarded as an heroic and iconic moment in Texan and U.S. history}} | ||
| + | [[Lieutenant Colonel]] [[William Barret Travis]] now commanded the Texan regular army forces assigned to defend the old mission. In January 1836 he was ordered by the provisional government to Alamo with volunteers to reinforce the 189 who were already there. Travis arrived in San Antonio on February 3 with 29 reinforcements. He became the post's official commander, taking over from Col. [[James C. Neill]], who promised to return in 20 days after leaving to tend to a family illness. | ||
| − | + | Other men also assembled to help in the defensive effort, including a number of unofficial volunteers under the command of [[Jim Bowie]]. Bowie, after whom the "Bowie" knife is named, was already famous for his adventures and knife fights. Travis and Bowie often quarreled over issues of command and authority but as Bowie's health declined, Travis assumed overall command. | |
| − | [[ | + | At that time, the siege of Alamo was seen as a battle of American settlers against Mexicans but many of the ethnic Mexicans in Texas (called ''[[Tejano|Tejanos]]'') in fact also sided with the rebellion. This struggle was viewed in similar terms as the [[American Revolution]] of 1776. These Tejanos wanted Mexico to have a loose central government and supported [[states rights]] as expressed in the [[Mexican Constitution of 1824]]. One Tejano combatant at Alamo was Captain [[Juan Seguin|Juan Nepomuceno Seguín]], who was sent out as dispatch rider before the final assault. |
| − | + | Defenders of the Alamo came from many places besides Texas. The youngest was Galba Fuqua, 16; one of the oldest was Gordon C. Jennings, 57. The men came from 28 different countries and states. From [[Tennessee]], a small group of volunteers led by the famous hunter, politician and Indian fighter [[Davy Crockett]] accompanied by [[Micajah Autry]], a lawyer. A 12-man "Tennessee Mounted Volunteers" unit arrived at Alamo on February 8. Davy Crocket had resigned from politics having told the electorate that if they did not elect him they could go to hell and he would go to Texas! | |
| − | + | The "[[New Orleans, Louisiana|New Orleans]] Greys," came from that city to fight as [[infantry]] in the revolution. The two [[Company (military unit)|companies]] comprising Greys had participated in the Siege of Béxar in December. Most Greys then left San Antonio de Béxar for an expedition to [[Matamoros]] with the promise of taking the war to Mexico, two dozen remaining at the Alamo. | |
| − | The | + | The abrogation of the Constitution of 1824 was a key trigger for the revolt in general. Many white Anglo-Saxons in Texas had strong sympathies for independence or for union with the United States. Some may have wanted a return to the Old Constitution that had allowed them a large degree of self-determination. When the Texans defeated the Mexican garrison at the Alamo in December of 1835, their flag had the words "Independence" on it. Letters written from Alamo expressed that "all here are for independence." The famous letter from Travis referred to their "flag of Independence." Some 25 years after the battle, historian Reuben Potter claimed that reinstatement of the Constitution of 1824 was a primary objective, and Potter's comments have also been the source of a myth that the battle flag of the Alamo garrison was some sort of Mexican tricolor with "1824" on it. |
| − | Another | + | Another main factor behind the revolt was the fact that Santa Anna had abolished [[slavery]] in Mexico. This was a serious setback to many landowners, who now faced financial ruin. Texan independence or joining the Union would allow these people to retain their slaves. As a slave state, Texas would support the [[Confederate States of America]] during the [[American Civil War]]. |
| − | + | == Siege == | |
| − | + | Lt. Col. William Travis was able to dispatch riders before the battle of March 3 informing the Texas provisional government of his situation and requesting assistance. Sam Houston's Texas Army was not strong enough to fight through the Mexican Army and relieve the post. The Provisional Texas government was in disarray due to in-fighting among members. Travis sent several riders, including [[James Bonham]] (1808–1836), to Colonel [[James Fannin]] for help. Fannin (1804–1836), commander of 450 Texas forces at [[Goliad, Texas|Goliad]] 100 miles southeast of Alamo, attempted an unorganized relief march with 320 men and cannon February 28 to Alamo, but aborted the relief column due to poor transportation. Most men were slaughtered by a Mexican force after surrendering (the "[[Goliad Campaign|Goliad Massacre]]"). | |
| − | |||
| − | + | March 1, 32 Texans led by Capt. George Kimbell and John W. Smith from [[Gonzales]], slipped through Mexican lines and joined the defenders inside the Alamo. They were the only response to Travis' plea for help. The group became known as the "Immortal 32." A letter written by one of the 32, [[Isaac Millsaps]], details events inside Alamo on the night before the siege. | |
| − | + | ==Final assault== | |
| + | At the end of 12 days the number of Mexican forces attacking was reported as high as 4,000 to 5,000, but only 1,400 to 1,600 soldiers were used in the final assault. Approximately 6,500 soldiers had originally set out from San Luis Potosí, but [[illness]] and [[desertion]] had reduced the force. The Mexican [[siege]] was scientifically and professionally conducted in [[Napoleon]]ic style. After a 13-day period during which the defenders were tormented with bands blaring at night (including buglers sounding the no-mercy call ''[[El Degüello]]''), artillery fire, and an ever closing ring of Mexicans cutting off potential escape routes, Santa Anna planned the final assault for March 6. Santa Anna raised a blood red flag which made his message clear: No mercy would be given for defenders. | ||
| − | + | Lt. Col. Travis wrote in his final dispatches: "The enemy has demanded a surrender at discretion otherwise the garrison are to be put to the sword, if the fort is taken—I have answered their demand with a cannon shot, & our flag still waves proudly from the walls—I shall never surrender or retreat." | |
| − | + | The Mexican army attacked Alamo in four columns plus reserve and pursuit and security force, starting at 05:30 AM. The first column of 300 to 400 men led by Martín Perfecto de Cos moved towards northwest corner of Alamo. Second 380 men commanded by Col. Francisco Duque. Third column comprised 400 soldiers led by Col. José María Romero. Fourth column comprised 100 ''cazadores'' (light infantry) commanded by Col. Juan Morales. The attacking columns had to cover 200 to 300 yards (200 to 300 m) open ground before they could reach Alamo walls. To prevent attempted escape by fleeing Texans or reinforcements entering, Santa Anna placed 350 cavalry under Brig. Gen. Ramírez y Sesma to patrol the surrounding countryside. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Texans pushed back one of the attacking columns but Perfecto de Cos' column was able to breach Alamo's weak north wall quickly; the first defenders fell, among them William Barret Travis, who was killed by a shot to the head. The rest of Santa Anna's columns continued the assault while Perfecto de Cos's men flooded into the fortress. Alamo's defenders were spread too thin to adequately defend both the walls and the invading Mexicans. By 6:30 that morning, nearly all Alamo defenders had been slain in brutal hand-to-hand combat. Famous defender Jim Bowie is reported to have been bayoneted and shot to death in his cot. The battle, from initial assault to capture of the Alamo, lasted only an hour. A group of male survivors were executed after the battle, including, it is claimed, Davy Crockett. | |
| − | + | Victorious Mexicans released two dozen surviving women and children, Bowie's slave Sam and Travis' slave Joe after the battle. Joe spoke of seeing a slave named John killed in the Alamo assault and another black woman killed. Another reported survivor was Brigido Guerrero, Mexican army deserter who had joined the Texan cause. He was able to convince the Mexican soldiers that he had been a prisoner held against his will. Henry Wornell was reportedly able to escape the battle, but died from his wounds three months later. | |
| − | + | ==Casualties== | |
| − | + | ===Texan=== | |
| + | 183 to 250 Texan and Tejano bodies were found at Alamo after the battle; Santa Anna's official report dictated to his personal secretary Ramón Martínez Caro, stated 600 rebel bodies were found. Historians believe this to be a false claim. All but one were burned by the Mexicans; the sole exception being Gregorio Esparza, who was buried rather than burned because his brother Francisco had served as an ''activo'' who had fought under General Perfecto de Cos in Siege of Béxar. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Mexican=== |
| − | + | Santa Anna reported that he had suffered 70 dead and 300 wounded, while many Texan accounts claim that as many as 1,500 Mexican lives were lost. While many quickly dismiss Santa Anna's account as being unrealistic, the Texan account of 1,500 dead also lacks logic. | |
| − | + | Alamo historians agree that the Mexican attack force consisted of 1,400 - 1,600 men, a count of 1,500 sounds improbable. Commonly acceptable accounts by historians are the ones that place the number of 200 and number of initial Mexican wounded at 400. These losses, (43 percent casualties) would have been considered catastrophic by the Mexican Army. | |
==Texan Independence== | ==Texan Independence== | ||
| − | Texas | + | Texas declared independence on March 2. The delegates elected [[David G. Burnet]] as Provisional President and [[Lorenzo de Zavala]] as Vice-President. The men inside the Alamo probably never knew that this event had occurred. Houston still held his rank of supreme military commander. The Texan Army never numbered more than 2,000 men at the time of Alamo siege. Successive losses at Goliad, [[Battle of Refugio|Refugio]], Matamoros and San Antonio de Béxar, reduced the army to 1,000 men. |
| − | + | April 21, at [[Battle of San Jacinto]], Santa Anna's 1,250-strong force was defeated by [[Sam Houston's]] army of 910 men, who used now-famous battle cry, "Remember the Alamo!" Mexican losses for the day were 650 killed with 600 taken prisoner. Texan losses were nine killed and 18 wounded. Santa Anna was captured the following day, dressed in a common soldier's jacket, having discarded his finer clothing in hopes of escaping. He issued orders that all Mexican troops under the command of Vicente Filisola (1789–1850) and [[José Urrea|José de Urrea]] (1795–1849) were to pull back into Mexico. | |
| − | == | + | ==Line in the sand== |
| − | + | Legend has it that on March 3, 4, or March 5, Lt. Col. Travis drew a line in the sand with his sword inviting all those willing to stay, presumably to die, to cross over the line. Jim Bowie was carried across the line at his request. All but one defender crossed the line. [[Moses Rose|Louis Rose]], a French soldier who had fought under [[Napoleon]] in [[Russia]] before arriving in Texas, slipped out of the Alamo. He evaded Mexican forces by moving at night, then Rose took shelter with the family of William P. Zuber to whom he told the tale of his escape. In 1873, Zuber (his son) published a version of the story, which has not been historically documented. The phrase "drawing a line in the sand" has remained part of English, for taking a stand with no compromise. This account is narrated in Steven Kellerman's "The Yellow Rose of Texas," ''Journal of American Folklore.'' | |
| − | |||
| − | Before the war ended, Santa Anna ordered | + | Before the war ended, Santa Anna ordered a red flag be raised from San Fernando cathedral indicating to the defenders inside the Alamo that no quarter would be given. According to José Enrique de la Peña's diary, several defenders who had not been killed in the final assault on Alamo were captured by Col. [[Castrillón]] and presented to Santa Anna, who personally ordered their deaths. Davy Crockett may or may not have been one of the six, since this is disputed. De la Peña states that Crockett attempted to negotiate surrender with Santa Anna but was turned down on the grounds of 'no guarantees for traitors'. There is little evidence to support this. Some believe that Crockett went down struggling to stay alive when he was spotted by Santa Anna's army after the 12 day struggle. |
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | + | *Borroel, Roger. ''The Texan Revolution of 1936.'' East Chicago, IN: La Villita Pbns., 2002. ISBN 192879209X | |
| − | + | *Crisp, James E. ''Sleuthing the Alamo.'' New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 0195163494 | |
| − | + | *Davis, William C. ''Lone Star Rising: The Revolutionary Birth of the Texas Republic.'' New York, NY: Free Press, 2004. ISBN 0684865106 | |
| − | + | *Dingus, Anne, ''The Truth About Texas.'' Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing Company, 1995. ISBN 0877192820 | |
| − | + | *Hardin, Stephen L. ''The Alamo 1836.'' Santa Anna's Texas Campaign, Osprey Campaign Series #89, Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2001. ISBN 1841760900 | |
| − | + | *Hardin, Stephen L. ''Texian Iliad.'' Austin, TX: University of Texas Press, 1994. ISBN 0292730861 | |
| − | + | *Lord, Walter. ''A Time to Stand.'' Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 1961. ISBN 0803279027 | |
| − | + | *Nofi, Albert A. ''The Alamo and The Texas War for Independence.'' Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 1992. ISBN 0306810409 | |
| − | + | *Rosenthal, Philip S. ''Alamo Soldiers: An Armchair Historian's Guide to the Defenders of the Alamo.'' A Team Productions, 1989. ISBN 096225570X | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | *Dingus, Anne, ''The Truth About Texas | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | *Hardin, Stephen L. | ||
| − | *Lord, Walter | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | *Rosenthal, Philip S. | ||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | * [http://www.thealamo.org/ The official page for the Alamo Site includes information on visiting the Alamo and historical background] | + | All links retrieved January 16, 2022. |
| − | + | * [http://www.thealamo.org/ The official page for the Alamo Site includes information on visiting the Alamo and historical background] | |
| − | + | * [http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=11841 Defenders of the Alamo Memorial] at Find A Grave | |
| − | + | * [http://texashistory.unt.edu/young/educators/alamo/index.shtml Remember the Alamo] a Primary Source Adventure, with lesson plans for Texas and American history, hosted by the Portal to Texas History. | |
| − | * [http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=11841 Defenders of the Alamo Memorial at Find A Grave | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * [http://texashistory.unt.edu/young/educators/alamo/index.shtml Remember the Alamo] a Primary Source Adventure, with lesson plans for Texas and American history, hosted by the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:History]] | [[Category:History]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:History of the Americas]] | |
{{credit|68955794}} | {{credit|68955794}} | ||
Revision as of 21:54, 16 January 2022
The Battle of the Alamo was a nineteenth century battle between the Republic of Mexico and the rebel Texan forces during the latter's fight for independence - the Texas Revolution. It took place at the Alamo mission in San Antonio, Texas (then known as "San Antonio de Béxar") in February and March of 1836. The 13-day siege ended on March 6 with the capture of the mission and the death of nearly all the Texan defenders, except for a few slaves, women and children. Despite the loss, the 13-day holdout stalled Mexican forces' progress and allowed Sam Houston to gather troops and supplies for his later successful battle at San Jacinto. Approximately 189 defenders were attacked by about 4,000 Mexican soldiers.
The battle took place at a turning point in the Texas Revolution, which had begun with the October 1835 Consultation whose delegates narrowly approved a call for rights under the Mexican Constitution of 1824. By the time of the battle, however, sympathy for declaring a Republic of Texas had grown. The delegates from the Alamo to the Constitutional Convention were both instructed to vote for independence. The deaths of such popular figures as Davy Crockett and Jim Bowie at the Alamo contributed to how the siege has subsequently been regarded as an heroic and iconic moment in Texan and U.S. history, notwithstanding that the Alamo fell. Texas' independence and its eventual union with the U.S. would have been unlikely had Mexico succeeeded in its plan to reassert sovereignty over the territory, which later would contribute enormously to the U.S. economy.
Prelude
Texas was part of the Mexican colony of New Spain. After the Mexican independence in 1821, Texas became part of Mexico. In 1824 it became the northern section of Coahuila y Tejas. January 3, 1823, Stephen F. Austin began a colony of 300 American families along the Brazos River in present-day Fort Bend County and Brazoria County, primarily in the area of what is now Sugar Land.
In 1835 the Mexican President and General Antonio López de Santa Anna Pérez de Lebrón, (known as Santa Anna) abolished the Constitution of 1824 and proclaimed a new constitution that increased the power of the Presidency and reduced the power of provincial governments. Since the end of hostilities with Spain ten years before, the Mexican government generally and Santa Anna in particular, had been eager to reassert control over entire country and control of Texas. This was seen as important as Santa Anna perceived the province to be vulnerable to America's westward expansion, which was in fact the case.
Mexico's new interest in Texas was not popular with the colonists, who felt themselves to be more economically and culturally linked to the United States than to Mexico. They were also used to the relative autonomy they enjoyed under the old Constitution of 1824. Santa Anna's increasingly ambitious seizure of dictatorial powers under the new constitution was causing unrest throughout Mexico. Hostilities in Texas began with the Battle of Gonzales, October 1, 1835 after which Texan rebels quickly captured Mexican positions at Goliad (La Bahía) and San Antonio.
After the surrender of General Martín Perfecto de Cos and his garrison at San Antonio, there was no longer a Mexican military presence in Texas. Santa Anna decided to launch an offensive to put down the rebellion. Minister of War José María Tornel and Maj. Gen. Vicente Filisola (1789–1850) proposed a seaborne attack to Santa Anna, which would have been easier for the troops. Since 1814, sea access had been the proven means of expeditions into Texas. Santa Anna refused this plan because it would take too long and, in the meantime, the rebels in Texas might receive aid from the United States.
Santa Anna assembled an estimated force of 6,100 soldiers and 20 cannons at San Luis Potosí in early 1836 and moved through Saltillo, Coahuila, towards Texas. His army marched across the Rio Grande through inclemental weather and snowstorms to suppress the rebellion. San Antonio de Béxar was one of his intermediate objectives; his ultimate objective was to destroy the Texas government and to restore rule of the central or "Centralist" Mexican government over a rebellious state. He had already suppressed a rebellion in the state of Zacatecas in 1835.
Santa Anna and his army arrived in San Antonio de Béxar on February 23, a mixed force of regular infantry and cavalry units and activo reserve infantry battalions. They were equipped with British Baker and out-dated, short range but effective and deadly British Tower Musket, Mark III, or "Brown Bess" muskets. The average Mexican soldier stood 5 feet, 1 inch; many were recent conscripts with no previous combat experience. Although well-drilled, the Mexican army discouraged individual marksmanship. Initial forces were equipped with four 7 inch howitzers, seven 4-pound, four 6-pound, four 8-pound, and two 12-pound cannons.
Many Mexican officers were foreign mercenary veterans, including Vicente Filisola (Italy) and Antonio Gaona (Cuba), while General Santa Anna was a veteran of Mexican War of Independence.
Defenders
Lieutenant Colonel William Barret Travis now commanded the Texan regular army forces assigned to defend the old mission. In January 1836 he was ordered by the provisional government to Alamo with volunteers to reinforce the 189 who were already there. Travis arrived in San Antonio on February 3 with 29 reinforcements. He became the post's official commander, taking over from Col. James C. Neill, who promised to return in 20 days after leaving to tend to a family illness.
Other men also assembled to help in the defensive effort, including a number of unofficial volunteers under the command of Jim Bowie. Bowie, after whom the "Bowie" knife is named, was already famous for his adventures and knife fights. Travis and Bowie often quarreled over issues of command and authority but as Bowie's health declined, Travis assumed overall command.
At that time, the siege of Alamo was seen as a battle of American settlers against Mexicans but many of the ethnic Mexicans in Texas (called Tejanos) in fact also sided with the rebellion. This struggle was viewed in similar terms as the American Revolution of 1776. These Tejanos wanted Mexico to have a loose central government and supported states rights as expressed in the Mexican Constitution of 1824. One Tejano combatant at Alamo was Captain Juan Nepomuceno Seguín, who was sent out as dispatch rider before the final assault.
Defenders of the Alamo came from many places besides Texas. The youngest was Galba Fuqua, 16; one of the oldest was Gordon C. Jennings, 57. The men came from 28 different countries and states. From Tennessee, a small group of volunteers led by the famous hunter, politician and Indian fighter Davy Crockett accompanied by Micajah Autry, a lawyer. A 12-man "Tennessee Mounted Volunteers" unit arrived at Alamo on February 8. Davy Crocket had resigned from politics having told the electorate that if they did not elect him they could go to hell and he would go to Texas!
The "New Orleans Greys," came from that city to fight as infantry in the revolution. The two companies comprising Greys had participated in the Siege of Béxar in December. Most Greys then left San Antonio de Béxar for an expedition to Matamoros with the promise of taking the war to Mexico, two dozen remaining at the Alamo.
The abrogation of the Constitution of 1824 was a key trigger for the revolt in general. Many white Anglo-Saxons in Texas had strong sympathies for independence or for union with the United States. Some may have wanted a return to the Old Constitution that had allowed them a large degree of self-determination. When the Texans defeated the Mexican garrison at the Alamo in December of 1835, their flag had the words "Independence" on it. Letters written from Alamo expressed that "all here are for independence." The famous letter from Travis referred to their "flag of Independence." Some 25 years after the battle, historian Reuben Potter claimed that reinstatement of the Constitution of 1824 was a primary objective, and Potter's comments have also been the source of a myth that the battle flag of the Alamo garrison was some sort of Mexican tricolor with "1824" on it.
Another main factor behind the revolt was the fact that Santa Anna had abolished slavery in Mexico. This was a serious setback to many landowners, who now faced financial ruin. Texan independence or joining the Union would allow these people to retain their slaves. As a slave state, Texas would support the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.
Siege
Lt. Col. William Travis was able to dispatch riders before the battle of March 3 informing the Texas provisional government of his situation and requesting assistance. Sam Houston's Texas Army was not strong enough to fight through the Mexican Army and relieve the post. The Provisional Texas government was in disarray due to in-fighting among members. Travis sent several riders, including James Bonham (1808–1836), to Colonel James Fannin for help. Fannin (1804–1836), commander of 450 Texas forces at Goliad 100 miles southeast of Alamo, attempted an unorganized relief march with 320 men and cannon February 28 to Alamo, but aborted the relief column due to poor transportation. Most men were slaughtered by a Mexican force after surrendering (the "Goliad Massacre").
March 1, 32 Texans led by Capt. George Kimbell and John W. Smith from Gonzales, slipped through Mexican lines and joined the defenders inside the Alamo. They were the only response to Travis' plea for help. The group became known as the "Immortal 32." A letter written by one of the 32, Isaac Millsaps, details events inside Alamo on the night before the siege.
Final assault
At the end of 12 days the number of Mexican forces attacking was reported as high as 4,000 to 5,000, but only 1,400 to 1,600 soldiers were used in the final assault. Approximately 6,500 soldiers had originally set out from San Luis Potosí, but illness and desertion had reduced the force. The Mexican siege was scientifically and professionally conducted in Napoleonic style. After a 13-day period during which the defenders were tormented with bands blaring at night (including buglers sounding the no-mercy call El Degüello), artillery fire, and an ever closing ring of Mexicans cutting off potential escape routes, Santa Anna planned the final assault for March 6. Santa Anna raised a blood red flag which made his message clear: No mercy would be given for defenders.
Lt. Col. Travis wrote in his final dispatches: "The enemy has demanded a surrender at discretion otherwise the garrison are to be put to the sword, if the fort is taken—I have answered their demand with a cannon shot, & our flag still waves proudly from the walls—I shall never surrender or retreat."
The Mexican army attacked Alamo in four columns plus reserve and pursuit and security force, starting at 05:30 AM. The first column of 300 to 400 men led by Martín Perfecto de Cos moved towards northwest corner of Alamo. Second 380 men commanded by Col. Francisco Duque. Third column comprised 400 soldiers led by Col. José María Romero. Fourth column comprised 100 cazadores (light infantry) commanded by Col. Juan Morales. The attacking columns had to cover 200 to 300 yards (200 to 300 m) open ground before they could reach Alamo walls. To prevent attempted escape by fleeing Texans or reinforcements entering, Santa Anna placed 350 cavalry under Brig. Gen. Ramírez y Sesma to patrol the surrounding countryside.
Texans pushed back one of the attacking columns but Perfecto de Cos' column was able to breach Alamo's weak north wall quickly; the first defenders fell, among them William Barret Travis, who was killed by a shot to the head. The rest of Santa Anna's columns continued the assault while Perfecto de Cos's men flooded into the fortress. Alamo's defenders were spread too thin to adequately defend both the walls and the invading Mexicans. By 6:30 that morning, nearly all Alamo defenders had been slain in brutal hand-to-hand combat. Famous defender Jim Bowie is reported to have been bayoneted and shot to death in his cot. The battle, from initial assault to capture of the Alamo, lasted only an hour. A group of male survivors were executed after the battle, including, it is claimed, Davy Crockett.
Victorious Mexicans released two dozen surviving women and children, Bowie's slave Sam and Travis' slave Joe after the battle. Joe spoke of seeing a slave named John killed in the Alamo assault and another black woman killed. Another reported survivor was Brigido Guerrero, Mexican army deserter who had joined the Texan cause. He was able to convince the Mexican soldiers that he had been a prisoner held against his will. Henry Wornell was reportedly able to escape the battle, but died from his wounds three months later.
Casualties
Texan
183 to 250 Texan and Tejano bodies were found at Alamo after the battle; Santa Anna's official report dictated to his personal secretary Ramón Martínez Caro, stated 600 rebel bodies were found. Historians believe this to be a false claim. All but one were burned by the Mexicans; the sole exception being Gregorio Esparza, who was buried rather than burned because his brother Francisco had served as an activo who had fought under General Perfecto de Cos in Siege of Béxar.
Mexican
Santa Anna reported that he had suffered 70 dead and 300 wounded, while many Texan accounts claim that as many as 1,500 Mexican lives were lost. While many quickly dismiss Santa Anna's account as being unrealistic, the Texan account of 1,500 dead also lacks logic.
Alamo historians agree that the Mexican attack force consisted of 1,400 - 1,600 men, a count of 1,500 sounds improbable. Commonly acceptable accounts by historians are the ones that place the number of 200 and number of initial Mexican wounded at 400. These losses, (43 percent casualties) would have been considered catastrophic by the Mexican Army.
Texan Independence
Texas declared independence on March 2. The delegates elected David G. Burnet as Provisional President and Lorenzo de Zavala as Vice-President. The men inside the Alamo probably never knew that this event had occurred. Houston still held his rank of supreme military commander. The Texan Army never numbered more than 2,000 men at the time of Alamo siege. Successive losses at Goliad, Refugio, Matamoros and San Antonio de Béxar, reduced the army to 1,000 men.
April 21, at Battle of San Jacinto, Santa Anna's 1,250-strong force was defeated by Sam Houston's army of 910 men, who used now-famous battle cry, "Remember the Alamo!" Mexican losses for the day were 650 killed with 600 taken prisoner. Texan losses were nine killed and 18 wounded. Santa Anna was captured the following day, dressed in a common soldier's jacket, having discarded his finer clothing in hopes of escaping. He issued orders that all Mexican troops under the command of Vicente Filisola (1789–1850) and José de Urrea (1795–1849) were to pull back into Mexico.
Line in the sand
Legend has it that on March 3, 4, or March 5, Lt. Col. Travis drew a line in the sand with his sword inviting all those willing to stay, presumably to die, to cross over the line. Jim Bowie was carried across the line at his request. All but one defender crossed the line. Louis Rose, a French soldier who had fought under Napoleon in Russia before arriving in Texas, slipped out of the Alamo. He evaded Mexican forces by moving at night, then Rose took shelter with the family of William P. Zuber to whom he told the tale of his escape. In 1873, Zuber (his son) published a version of the story, which has not been historically documented. The phrase "drawing a line in the sand" has remained part of English, for taking a stand with no compromise. This account is narrated in Steven Kellerman's "The Yellow Rose of Texas," Journal of American Folklore.
Before the war ended, Santa Anna ordered a red flag be raised from San Fernando cathedral indicating to the defenders inside the Alamo that no quarter would be given. According to José Enrique de la Peña's diary, several defenders who had not been killed in the final assault on Alamo were captured by Col. Castrillón and presented to Santa Anna, who personally ordered their deaths. Davy Crockett may or may not have been one of the six, since this is disputed. De la Peña states that Crockett attempted to negotiate surrender with Santa Anna but was turned down on the grounds of 'no guarantees for traitors'. There is little evidence to support this. Some believe that Crockett went down struggling to stay alive when he was spotted by Santa Anna's army after the 12 day struggle.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Borroel, Roger. The Texan Revolution of 1936. East Chicago, IN: La Villita Pbns., 2002. ISBN 192879209X
- Crisp, James E. Sleuthing the Alamo. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 0195163494
- Davis, William C. Lone Star Rising: The Revolutionary Birth of the Texas Republic. New York, NY: Free Press, 2004. ISBN 0684865106
- Dingus, Anne, The Truth About Texas. Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing Company, 1995. ISBN 0877192820
- Hardin, Stephen L. The Alamo 1836. Santa Anna's Texas Campaign, Osprey Campaign Series #89, Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2001. ISBN 1841760900
- Hardin, Stephen L. Texian Iliad. Austin, TX: University of Texas Press, 1994. ISBN 0292730861
- Lord, Walter. A Time to Stand. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 1961. ISBN 0803279027
- Nofi, Albert A. The Alamo and The Texas War for Independence. Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 1992. ISBN 0306810409
- Rosenthal, Philip S. Alamo Soldiers: An Armchair Historian's Guide to the Defenders of the Alamo. A Team Productions, 1989. ISBN 096225570X
External links
All links retrieved January 16, 2022.
- The official page for the Alamo Site includes information on visiting the Alamo and historical background
- Defenders of the Alamo Memorial at Find A Grave
- Remember the Alamo a Primary Source Adventure, with lesson plans for Texas and American history, hosted by the Portal to Texas History.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.