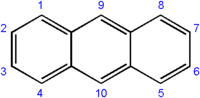
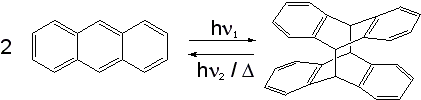Anthracene
| Anthracene | |
|---|---|
| |
| IUPAC name | Anthracene |
| Molecular formula | C14H10 |
| Molar mass | 178.23 g/mol |
| CAS number | [] |
| Density | 1.099 g/cm³ |
| Melting point |
217.5 °C |
| Boiling point |
340 °C |
| SMILES | c23cc1ccccc1cc2cccc3 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
In chemistry, anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of three benzene rings derived from coal-tar. Anthracene is used in the artificial production of the red dye alizarin. It is also used in wood preservatives, insecticides, and coating materials. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400-500nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
Synthesis
A classic method for the preparation of anthracene in the laboratory is by cyclodehydration of o-methyl- or o-methylene-substituted diarylketones in the so-called Elbs reaction (named for the German chemist Karl Elbs, born 13 September 1858 in Alt-Breisach, Baden, Germany, died 24 August 1933).
Reactions
Anthracene has the ability to photodimerize with irradiation by UV light. This results in considerable changes in the physical properties of the material.
The dimer is connected by two covalent bonds resulting from the [4+4] cycloaddition. The dimer reverts to anthracene thermally or with UV irradiation below 300 nm. The reversible bonding and photochromic properties of anthracenes is the basis of many potential applications using poly and monosubstituted anthracene derivatives. The reaction is sensitive to oxygen.
In most other reactions of anthracene, the central ring is also targeted, as it is the most highly reactive. Electrophilic substitution occurs at the "9" and "10" positions of the center ring, and oxidation of anthracene occurs readily, giving anthraquinone, C14H8O2 (below).
Uses
Anthracene can also have a hydroxyl group to form 1-hydroxyanthracene and 2-hydroxyanthracene, homologous to phenol and napthol, and hydroxyanthracene is also called anthrol, and anthracenol.[1][2] Hydroxyanthracene derivatives are pharmacologically active, and are contained in aloe for example.[3][4]
Anthracene is an organic semiconductor.
Anthracene is used as a scintillator for detectors of high energy photons, electrons and alpha particles. Plastics such as polyvinyltolulene can be doped with Anthracene to produce a plastic scintillator that is approximately water equivalent for use in radiation therapy dosimetry. Anthracenes emission spectrum peaks at between 400nm and 440nm.
See also
- Phenanthrene
- Tetracene
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0825 – International Occupational Safety and Health Information Centre, International Labour Organization.
- IARC Monograph "Anthracene."
- National Pollutant Inventory - Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Fact Sheet
- NIST Chemistry WebBook Anthracene
Template:ChemicalSources
cs:Antracen de:Anthracen es:Antraceno fr:Anthracène it:Antracene nl:Anthraceen ja:アントラセン pl:Antracen ru:Антрацен fi:Antraseeni vi:Anthracen uk:Антрацен zh:蒽